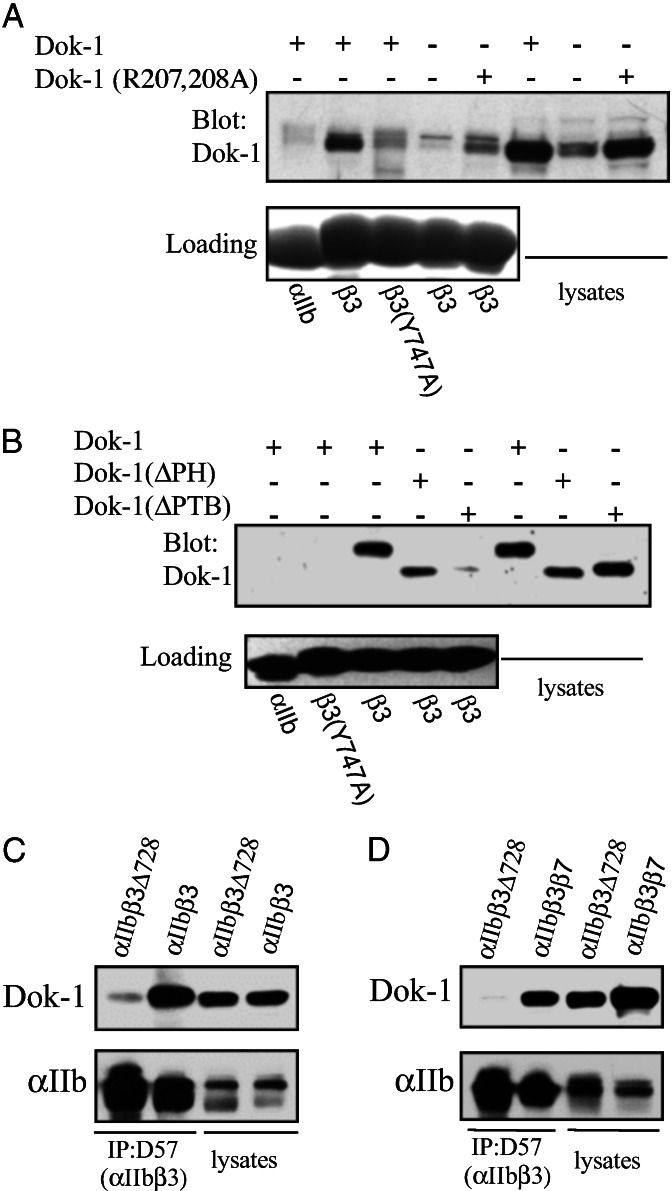
Figure 4.
Intact Dok-1 binds to integrin β tails. (A) Lysates from CHO cells transiently transfected with Dok-1, Dok-1 containing a mutation that reduces PTB domain ligand binding [Dok-1 (R207,208A; ref. 37], or from mock-transfected cells were incubated with beads coated with recombinant αIIb, β3, or β3(Y747A) cytoplasmic domains. Bound proteins were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and Dok-1 was detected by Western blotting with anti-Dok-1 antibodies. Note the specific binding of a band in the untransfected cells, presumably that of endogenous hamster Dok-1. (B) Lysates from CHO cells transiently transfected with epitope-tagged Dok-1, Dok-1 lacking its PH domain [Dok-1(ΔPH)], or Dok-1 lacking its PTB domain [Dok-1(ΔPTB)] were incubated with beads coated with recombinant αIIb, β3, or β3(Y747A) cytoplasmic domains. Bound proteins were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and Dok-1 was detected by Western blotting with antibodies against the epitope tags. (C) CHO cells stably expressing αIIbβ3 or αIIbβ3Δ728 were transfected with Dok-1, and 24 h later cells were lysed and the integrins were precipitated with the mAb D57. Immunoprecipitated αIIb and coimmunoprecipitated Dok-1 were detected by Western blotting. (D) CHO cells stably expressing αIIbβ3β7 or αIIbβ3Δ728 were transfected with Dok-1, and 24 h later cells were lysed and the integrins were precipitated with the mAb D57. Immunoprecipitated αIIb and coimmunoprecipitated Dok-1 were detected by Western blotting.