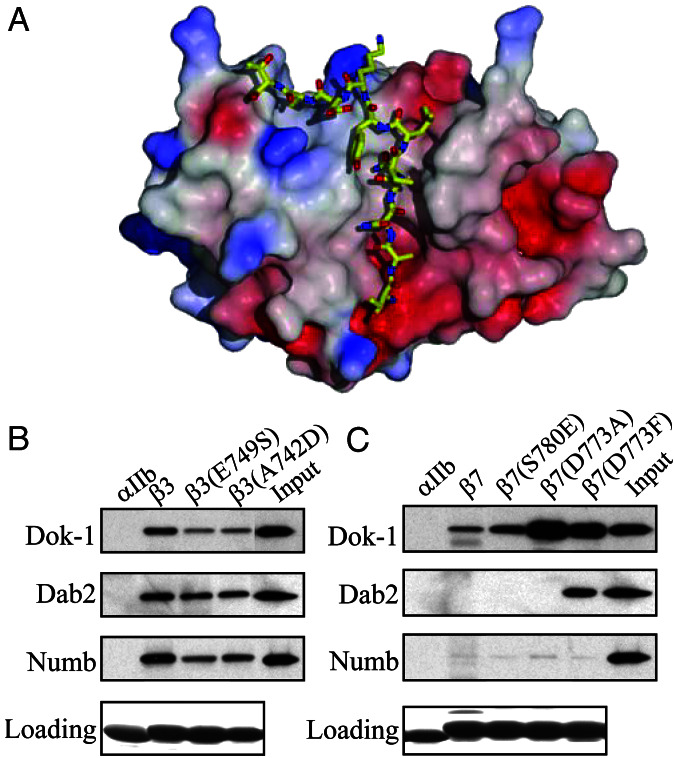
Figure 5.
Mutations in β integrin cytoplasmic tails alter PTB domain-binding specificity. (A) Structural modeling of the interaction between the Numb PTB domain and the β3 integrin cytoplasmic tail. A model of β3 residues Thr-741 to Thr-751 docked in the Numb-PTB domain binding site was generated based on the structure of the Numb–Nak complex. (B) Introduction of a charged residue at the −5 position and a noncharged residue at the +2 position relative to the Tyr or the β3 NPXY motif inhibit PTB domain binding. GST-PTB domain fusion proteins were incubated with beads coated with recombinant β3, β3(E749S), or β3(A742D) tails. Bound proteins were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and GST-PTB domains were detected by Western blotting with anti-GST antibodies. Loading of the recombinant integrin tails on the beads was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. (C) Introduction of an uncharged residue at the −5 position and a charged residue at the +2 position relative to the Tyr or the β7 NPXY motif enhances PTB domain binding. The binding of recombinant GST-PTB domain fusion proteins to β7, β7(S780E), β7(D773A), or β7(D773F) integrin cytoplasmic tails was assessed as described in B.