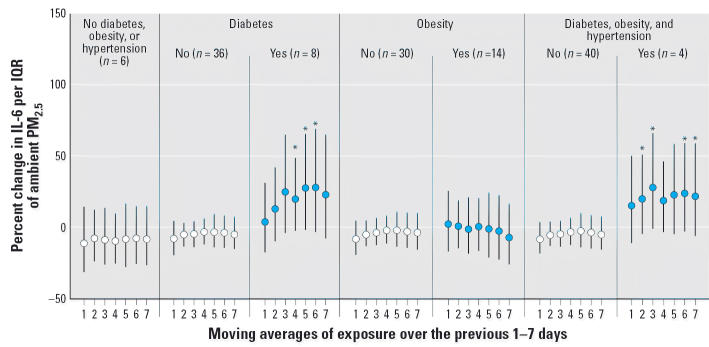
Figure 3.
Effect modification of associations between ambient PM2.5 and IL-6 by risk factor (n = number of individuals). All models were adjusted for sex, diabetes, obesity, smoking history, ambient and microenvironmental apparent temperature, trip, pollen, mold, hour, and vitamin use. Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
*Statistically significant interaction at the 95% confidence level.