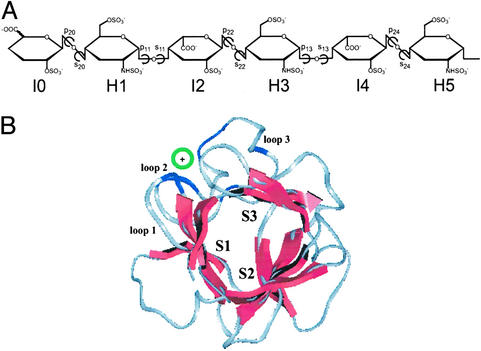
Figure 1.
FGF–HSGAG structural complex. (A) Chemical structure of HSGAG oligosaccharide observed in all of the FGF–HSGAG cocrystal structures. The units are numbered from nonreducing to reducing end. The glycosidic torsion angles are pij (C2j-C1j-Oj-C4j) and sij (C1j-Oj-C4j-C3j), where i = 1 for an H-I linkage and 2 for an I-H linkage, and j is the monosaccharide number. (B) Orientation and chain direction of the HSGAG oligosaccharide relative to sheets S1, S2, and S3 (red) of a β-trefoil scaffold of FGF whose Cα trace is such that the pseudoaxis of threefold symmetry is roughly perpendicular to the plane of the paper. The orientation of the oligosaccharide (indicated by green circle) is at a slight angle to the plane of the paper between S1 and S3. The oligosaccharide interacts with the basic residues (blue) in the loop regions (in gray, numbered 1–3). The observed chain directions are such that either the nonreducing or reducing end is projecting out of the plane of the paper.