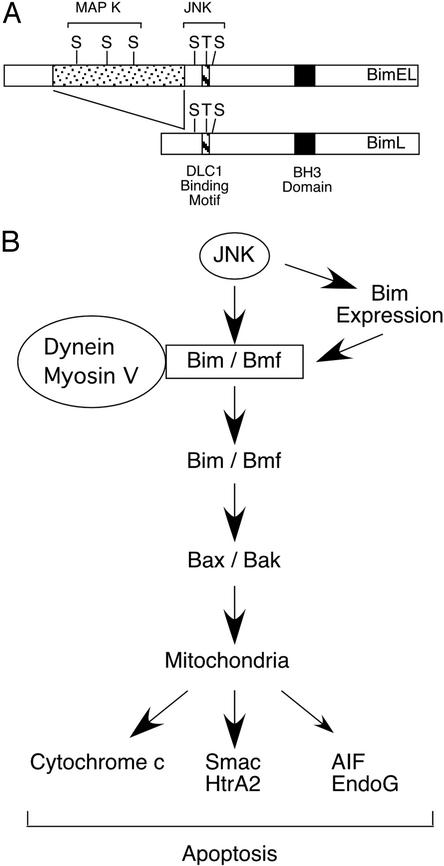
Figure 5.
A JNK-dependent apoptosis signaling pathway. (A) Schematic illustration of MAPK phosphorylation of BimL and BimEL. Two groups of MAPK sites were identified. Three Ser-Pro sites are phosphorylated by the ERK group of MAPK within the BimEL-specific insert region. In addition, three JNK phosphorylation sites are located within the common region of BimL and BimEL that is absent from BimS. Phosphorylation of Bim on Thr-56 causes dissociation from DLC1. (B) Schematic illustration of a JNK-dependent apoptosis signaling pathway. This signaling pathway is initiated by the phosphorylation of Bim and Bmf by JNK. In some cells, JNK may also contribute to Bim expression. The phosphorylation by JNK is proposed to cause the release of Bim and Bmf from dynein and myosin V motor complexes. The activated Bim and Bmf may directly activate Bax and Bak or may indirectly activate Bax and Bak by binding antiapoptotic Bcl2 family proteins (e.g., Bcl2 and Bcl-Xl). These mechanisms can lead to the engagement of the Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Smac, second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase; HtrA2, second homology of the bacterial HtrA endoprotease; AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; and EndoG, endonuclease G.