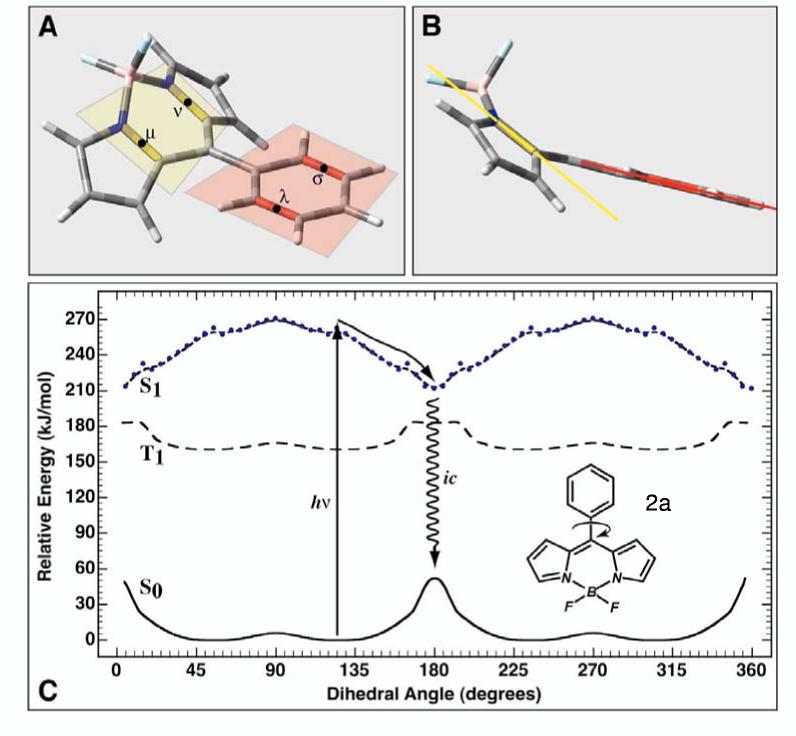
Figure 9.
The ground, first excited triplet state and first excited singlet state potential energy surfaces of 2a as a function of phenyl group rotation is shown in C. As the phenyl group rotates into the plane of the boron-dipyrrin framework, repulsions between the hydrogen atoms on both groups force a puckering as shown in A and B. This distortion requires that we define the angle of rotation with reference to the rotation of the yellow and red planes. In practice, the dihedral angle is calculated in terms of the bond centroids υ, ν, λ and σ as shown in insert A. The alignment shown in B represents a dihedral angle of 0° (which because of symmetry is identical to 180° or 360°). The ground and triplet state surfaces were calculated using B3LYP/6-31G(d) methods. The excited singlet state surface was calculated using full single CI minimization with a correlative correction calculated by using SACCI doubles (see text).