Table 2.RELATIVE HAZARD OF HAVING ONE OR MORE SUBSEQUENT BILIARY DRAINAGE PROCEDURES ASSOCIATED WITH INITIAL GALLBLADDER BYPASS COMPARED WITH BILE DUCT BYPASS
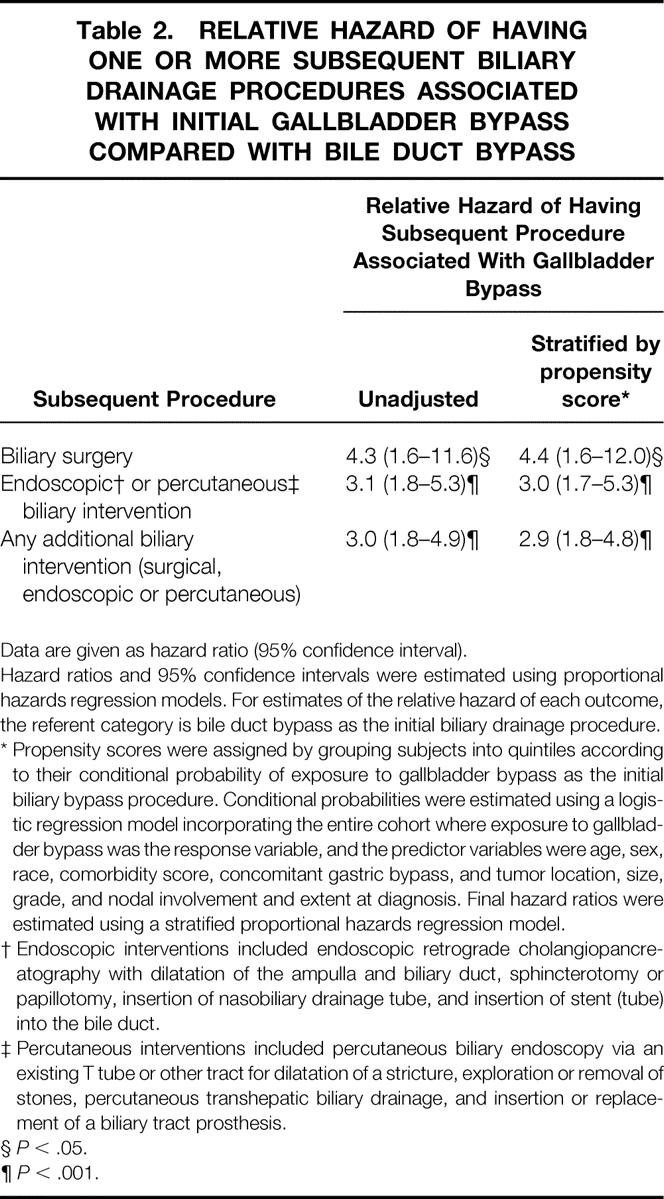
Data are given as hazard ratio (95% confidence interval).
Hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals were estimated using proportional hazards regression models. For estimates of the relative hazard of each outcome, the referent category is bile duct bypass as the initial biliary drainage procedure.
* Propensity scores were assigned by grouping subjects into quintiles according to their conditional probability of exposure to gallbladder bypass as the initial biliary bypass procedure. Conditional probabilities were estimated using a logistic regression model incorporating the entire cohort where exposure to gallbladder bypass was the response variable, and the predictor variables were age, sex, race, comorbidity score, concomitant gastric bypass, and tumor location, size, grade, and nodal involvement and extent at diagnosis. Final hazard ratios were estimated using a stratified proportional hazards regression model.
† Endoscopic interventions included endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with dilatation of the ampulla and biliary duct, sphincterotomy or papillotomy, insertion of nasobiliary drainage tube, and insertion of stent (tube) into the bile duct.
‡ Percutaneous interventions included percutaneous biliary endoscopy via an existing T tube or other tract for dilatation of a stricture, exploration or removal of stones, percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, and insertion or replacement of a biliary tract prosthesis.
§P < .05.
¶P < .001.
