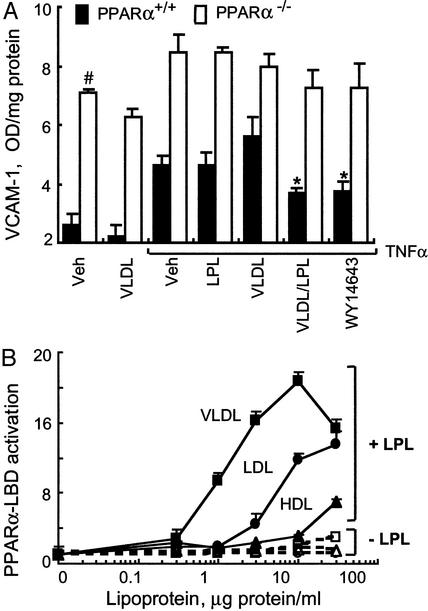
Figure 2.
LPL/VLDL inhibits VCAM1 levels through a PPARα-dependent mechanism. (A) VCAM1 surface expression in EC obtained from WT (filled bars) or PPARα−/− (open bars) mice was measured by ELISA as described (6). EC cultured in 96-well plates were treated as in Fig. 1A with murine TNFα (10 ng/ml, 18 h). Data represent absorbance at 410 nm after protein concentration normalization. In WT, but not PPARα−/−, EC both WY14643 and LPL/VLDL significantly decrease VCAM1 levels (*, P < 0.005). Basal VCAM1 levels in PPARα−/− are significantly increased as compared with WT EC (#, P < 0.001). (B) Concentration-dependent activation of PPARα-LBD by various lipoproteins in the presence or absence of LPL (30 units/ml). EC cotransfected with PPARα-LBD, the luciferase response pUASx4-TK-luc, and β-galactosidase constructs were stimulated as shown (18 h, DMEM, 1% delipidated serum). PPARα-LBD activation by fenofibric acid (100 μM) in this experiment was 16.2- ± 1.3-fold.