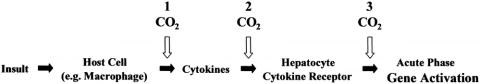
Figure 4. Mechanism of hepatic acute phase gene activation following intra-abdominal insult. CO2 pneumoperitoneum may attenuate this inflammatory response cascade by acting at any of a number of different steps: (1) CO2 may cause local peritoneal cell acidosis, thus blocking the release of cytokines; (2) CO2 may influence the clearance of circulating inflammatory mediators or alter cytokine–cytokine receptor interactions in the liver and elsewhere; or (3) hepatocytes may be affected directly by CO2 via alterations in second messenger system function or transcription factor action.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.