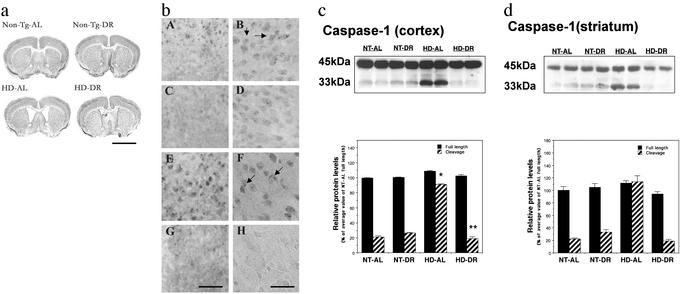
Figure 2.
DR reduces brain atrophy, decreases huntingtin aggregate formation, and inhibits caspase-1 activation in HD mice. (a) Photomicrographs of brain sections of 20-wk-old HD mice and nontransgenic mice (Non-Tg) that had been maintained on AL or DR regimens for 3 mo. Brain sections were stained with cresyl violet. The enlargement of lateral ventricles in HD mice is reduced in HD mice maintained on DR. Scale bar: 4 mm. The examples presented are representative of all six mice examined in each group. (b) Brain sections from 20-wk-old mice were immunostained with EM-48 antibody, which recognizes mutant human huntingtin N-terminal fragment. Intranuclear inclusions of mutant huntingtin (arrows) were abundant in the cortex (bA and bB) and striatum (bE and bF) of HD mice fed AL. The number of cells with intranuclear inclusions was decreased in the cortex (bC and bD) and striatum (bG and bH) of HD mice that had been maintained on DR compared with those fed AL. Scale bars: 125 μm in bG (bA, bC, and bE), 50 μm in bH (bB, bD, and bF). The results presented are representative of all six mice examined in each group. (c and d) Immunoblots of proteins in samples of cortical and striatal tissue (50 μg per lane) from the indicated genotype and diet groups. (Upper) Representative blots with caspase-1 antibody, which recognize full length of caspase-1 (45 kDa) and cleavage product (33 kDa) in cortex (c) and striatum (d). (Lower) Densitometric analysis results of blots (n = 4 mice per group). *, P < 0.01 compared with the value for nontransgenic (NT)-AL 33-kDa cleavage product; **, P < 0.01 compared with the value for the HD-AL 33-kDa cleavage product. ANOVA with Scheffé post hoc tests.