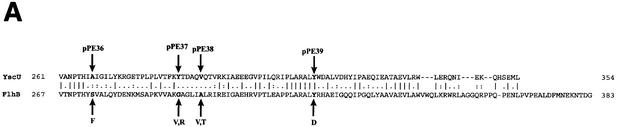
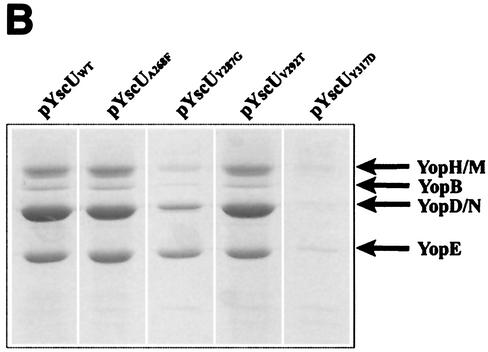
FIG. 3.
yscU mutants. (A) Alignment of the C-terminal-most amino acid sequences of YscU of Y. pseudotuberculosis and of FlhB of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. A pairwise alignment was performed with the EMBOSS alignment tool at the homepage of the European Bioinformatics Institute (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/emboss/align). Indicated in boldface are the extragenic suppressors in flhB of polyhook first-site mutations in fliK as described by Williams et al. (51) and the single-site mutations in yscU generated and utilized in this study. The mutations in FlhB are S274F (F), G293V and G293R (V,R), A298V and A298T (V,T), and Y323D (D). In YscU, the mutations are A268F(pPE36), Y287G(pPE37), V292T(pPE38), and Y317D(pPE39). (B) Yop secretion by different yscU mutants. Mutations in the cytoplasmic region of YscU were introduced in trans into the yscU-null strain YPIII(pIB75). Expression of YscU was under the control of the tac promoter, which was not induced with IPTG in these experiments. Bacteria were grown at 37°C in BHI medium lacking calcium to induce secretion. Cultures were centrifuged to separate the supernatant and cell pellet fractions. Equal amounts of supernatant fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. The mutations introduced into the cytoplasmic region of YscU were based on those studied by Macnab and colleagues (Fig. 3A) (51). The positions of these sites are indicated in the figure. WT, wild type.