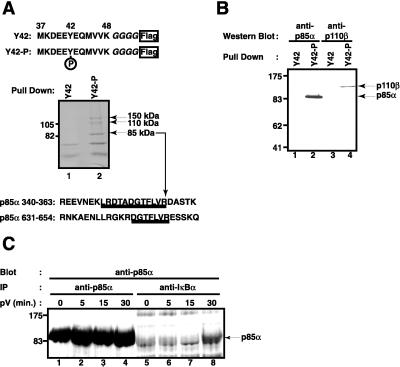
Figure 1.
Proteins interacting with a tyrosine-phosphorylated IκB-α peptide. (A) Affinity purification. The sequence of the peptides used for the affinity purification from 293 cell extracts is shown on top. Amino acid residues 37–48 of IκB-α were fused to four glycine residues and a Flag epitope at the C terminus. Tyrosine 42 was either phosphorylated (Y42-P) or not (Y42). Proteins interacting with the nonphosphorylated peptide (lane 1) or the phosphorylated peptide (lane 2) were analyzed by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Coomassie blue staining. The position of two molecular mass markers is indicated on the left; the position of three proteins interacting only with the tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide is indicated on the right. Protein sequences of two tryptic peptides obtained from the 85-kDa band are shown underlined. They are found within the indicated regions of human PI3-kinase regulatory p85α subunit. (B) Both PI3-kinase subunits bind to the IκB-α peptide. Proteins from Jurkat T cells binding to the nonphosphorylated peptide (lanes 1 and 3) or tyrosine-phosphorylated IκB-α peptide (lanes 2 and 4) were analyzed by Western blotting using an antibody directed against the regulatory p85α subunit of PI3-kinase (lanes 1 and 2) or the catalytic p110β subunit of PI3-kinase (lanes 3 and 4). The positions of p85α and p110β are indicated by arrows on the right; the positions of four molecular mass markers on the left. (C) Interaction of endogenous p85α with endogenous IκB-α on pV treatment. Jurkat T cells (1.5 × 106) pretreated with 400 nM wortmannin were induced with 400 μM pV for 0 (lanes 1 and 5), 5 (lanes 2 and 6), 15 (lanes 3 and 7), and 30 min (lanes 4 and 8). Cytosolic extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti-p85α (lanes 1–4) or anti-IκB-α (lanes 5–8). The presence of p85α in the complexes was detected by Western blotting. The position of p85α is indicated by an arrow.