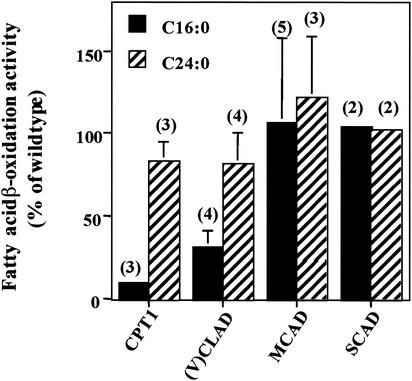
FIG. 2.
LCFA (C16:0) and VLCFA (C24:0) β-oxidation activities were measured in fibroblasts with a reduced capacity for mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation. Fibroblasts lacking either (i) CPT1, i.e., the ability to transport LCFA across the mitochondrial membrane, or (ii) (V)LCAD, i.e., the ability to metabolize LCFA, had reduced rates of LCFA (C16:0) and peroxisomal VLCFA (C24:0) β-oxidation. Fibroblasts with mutations affecting MCAD and SCAD β-oxidation had normal rates of both LCFA (C16:0) and peroxisomal VLCFA (C24:0) β-oxidation. Wild-type fatty acid β-oxidation was determined in each experiment as described in Materials and Methods, and this value was used to calculate the percentage of wild-type activity in the fibroblast cell lines being studied. Results are shown as means ± the standard deviations with the number of experiments performed in parentheses.