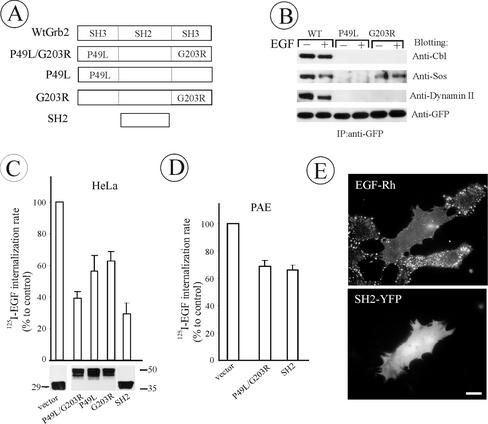
Figure 7.
The effect of Grb2 mutant overexpression on EGFR internalization in HeLa and PAE cells. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type and mutant Grb2 fusion proteins. YFP or CFP was attached to the carboxyl-terminus of Grb2 mutants (unpublished data). (B) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with WtGrb2-YFP, P49L-Grb2-YFP, or G203R-Grb2-YFP. After 36–48 h transfection, cells were either left untreated or stimulated with 1 ng/ml EGF for 5 min at 37°C. YFP-fusion proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with anti-GFP and immunoblotted with antibodies to c-Cbl, Sos-1/2, dynamin 2, and GFP. (C) HeLa cells transiently transfected with Grb2 mutants were incubated with 1 ng/ml 125I-EGF at 37°C, and the ke values were measured and expressed as percent of the value obtained for the vector-transfected cells. The level of expression (bottom) and transfection efficiency (unpublished data) were monitored, respectively, by Western blotting of cell lysates with anti-GFP and by imaging the YFP fluorescence of confluent cells before internalization assays and were similar for different Grb2 mutants. (D) 125I-EGF internalization rates in PAE cells tran-siently expressing Grb2 mutants were measured and expressed as in C. (F) PAE cells expressing wild-type EGFR were transfected with SH2-YFP. Two days later, the cells were incubated with EGF-Rh (1 ng/ml) for 1 h at 4°C, washed, and further incubated for 6 min at 37°C. The images were acquired from living cells through Cy3 filters. Bar, 10 μm. All data in the figure represent the mean values obtained from at least three independent experiments, and the error bars represent SE of the mean.