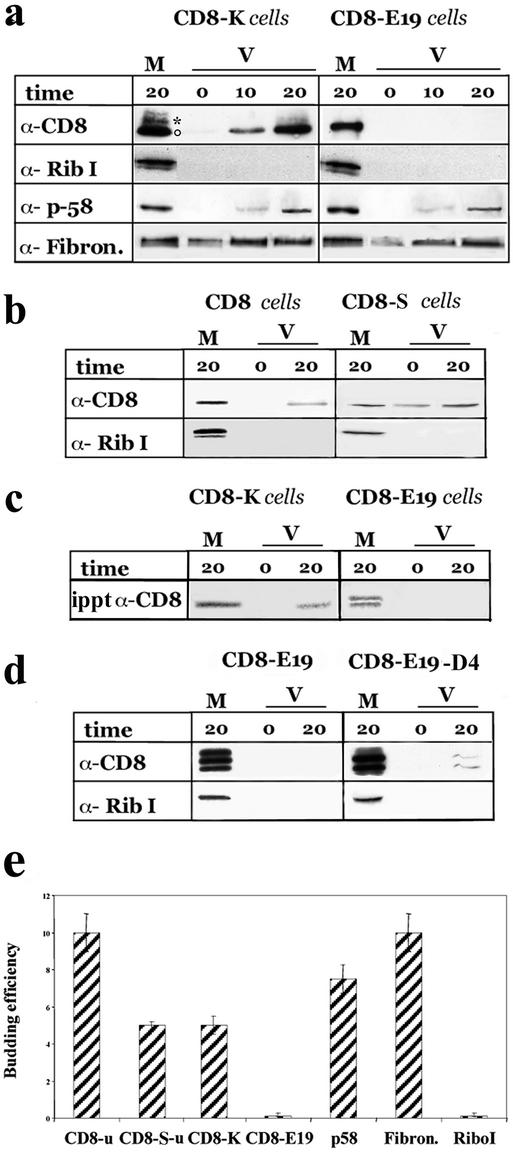
Figure 1.
CD8-K, but not CD8-E19, is efficiently exported from the ER in vitro. (a) Total microsomal fractions from cells stably expressing CD8-K or CDE19 were used to program budding assays in vitro as detailed in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The incubations were performed for the indicated times (in minutes; 0 indicates samples incubated on ice for 20 min) and then the microsomal (M) and the vesicular (V) fractions were separated by differential centrifugation and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblot to detect theindicated proteins. One-tenth of the M and 100% of the V fractions were loaded on the gels. The experiment shown is representative of seven and three independent assays for CD8-K and CD8-E19, respectively. ○ and * indicate the position on the gels of the nonglycosylated and initially glycosylated forms of CD8-K, respectively. (b) Total microsomal fraction from cells stably expressing CD8 and CD8-S were used for budding assay as described above. One-tenth of M and one entire V fraction, and one-half of M and three V fractions were loaded on the gels to detect CD8u and CD8-Su, respectively. Only the portions of the blots containing the nonglycosylated forms of the two proteins were analyzed. (c) Cells stably expressing CD8-K and CD8-E19 were radiolabeled for 20 min with [35S]cysteine and methionine and then used for the budding assay. The M and V fractions were lysed with 1% SDS, subjected to immunoprecipitation, and the total immunoprecipitated products were loaded on the gel. The dried gel was exposed for 3 d to a PhosphorImager (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) screen. (d) FRT cells were transiently transfected with pT8E19 or pT8D4, as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS and then used for the budding assay. One hundred percent of the M and V fractions were loaded on the gels. (e) Quantitation of budding efficiency of each protein recovered in the V fraction with respect to the total (M + V fractions). Only the results obtained with assays from stably expressing cells analyzed by immunoblotting are reported. Different exposures of the immunoblots were analyzed with the NIH Image program (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). The percentage of protein measured in the V fraction of incubations held on ice was subtracted from the corresponding incubations performed at 37°C. SD is indicated (n = 3).