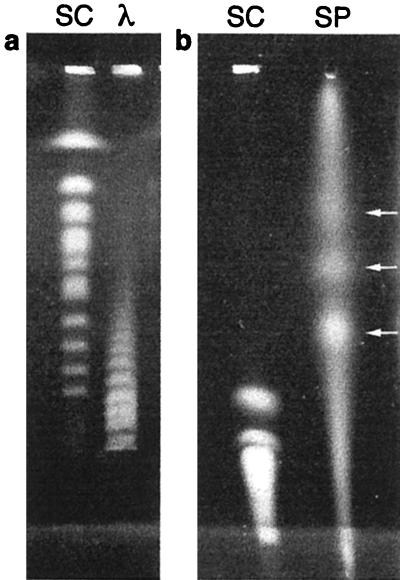
Figure 6.
Rotating-gel apparatus separations performed in 0.3% high-strength agarose gels (FMC Gold) cast inside supporting frames of 1% FastLane agarose. (a) S. cerevisiae chromosomes (0.25–2 Mbp) (SC) and λ concatemers (λ) separated in 4 hr by using an electric field of 7.5 V/cm and pulse times ramped from 20 to 45 sec. The two largest chromosomes (1.6 and 2 Mbp) comigrate in the top band. (b) Separation of S. cerevisiae (SC) and S. pombe (SP) chromosomes. The three S. pombe chromosomes (3.5, 4.7, and 5.7 Mbp) are indicated by arrows. To launch the chromosomes from the wells, a field-inversion electrophoresis protocol (30 sec forward, 10 sec backward) was applied for 2 hr, with a field of 1.2 V/cm. Then, 100 periodic rotations of 110° with shaped-field pulses were applied for 18 hr. Pulses started at 10 V/cm (after each rotation), but decayed as E(t) = (Tcrit/2μρefft)1/2, assuming Tcrit = 15 pN, ρeff = 0.084 e−/phosphate, and μ = 6 × 10−9 m2/V·sec.