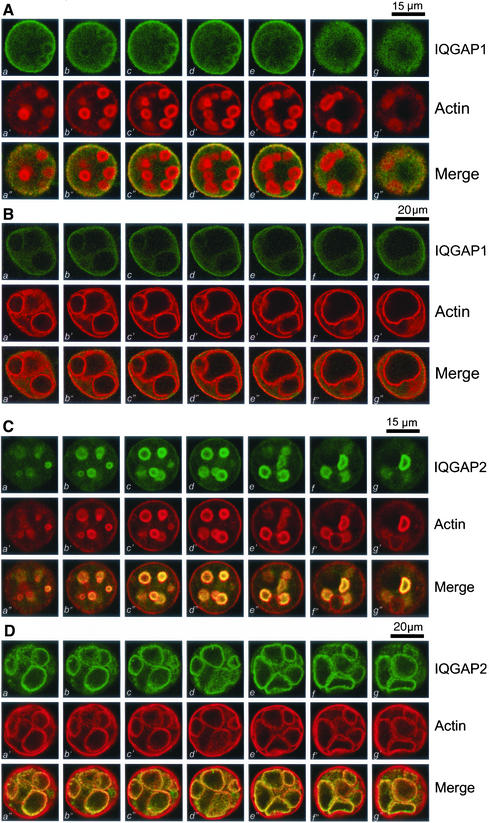
Figure 4.
Polarized distribution of IQGAP1 and IQGAP2 in resting and secreting parietal cells. (A) IQGAP1 is preferentially localized to the basolateral membrane of resting parietal cells. This triple montage represents a series of optical sections from the bottom (a, a′, and a") to the top (h, g′, and g"), of a resting gastric parietal cell doubly stained for IQGAP1 (green, a–g), F-actin (red, a′–g′), and their merges (a"–g"). IQGAP1 is mainly located to basolateral membrane surface and cytoplasm. Somewhat lighter staining of IQGAP1 can also been seen as rings, in a pattern of the suggestive of the invaginations of the apical plasma membrane forming the intracellular canaliculi. Bar, 15 μm. (B) This triple montage of a series of optical sections was arranged in a similar way to that of A, but the parietal cells were stimulated with histamine. Individual images from each focal plane of two fluorophores were collected and processed using Adobe Photoshop. Bar, 20 μm. (C) IQGAP2 is preferentially localized to the apical membrane of the parietal cells. This triple montage of optical sections is arranged similarly to that shown in A, but in this case the resting parietal cells were doubly stained for IQGAP2 (green, a–g), F-actin (red, a′–g′), and merged images. IQGAP2 is chiefly localized to the intracellular of parietal cells, with a distribution profile similar to that F-actin, except for the basolateral surface staining of F-actin. Bar, 15 μm. (D)This triple montage of a series of optical sections was arranged in a similar way to that of C, but in this case the parietal cells were stimulated with histamine. Bar, 20 μm.