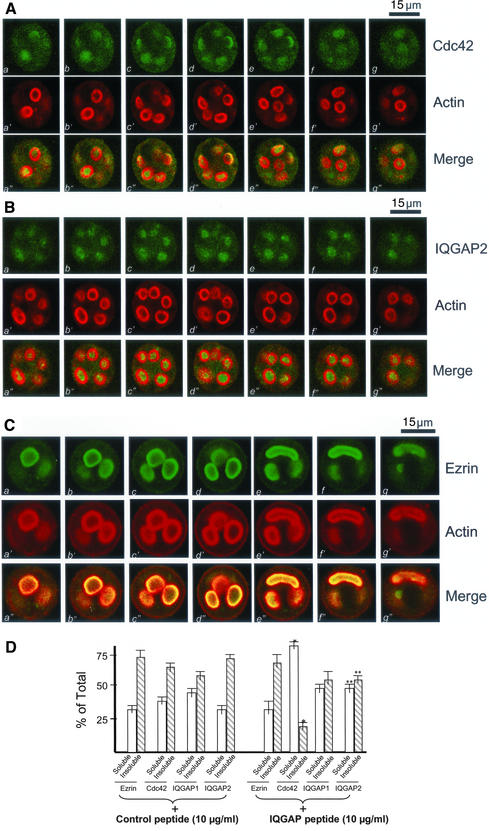
Figure 6.
IQGAP2 *Cdc42 interaction is required for the apical membrane remodeling associated with regulated secretion. (A) This triple montage of optical sections is arranged similarly to that shown in Figure 4, but in this case the peptide-treated, histamine-stimulated parietal cells were doubly stained for Cdc42 (green, a–g), F-actin (green, a′–g′), and merged images. Although F-actin is chiefly localized to the apical plasma membranes, the Cdc42 labeling is liberated from the apical vacuoles and diffused throughout the cytoplasm. Individual fluorescent images from each focal plane of two fluorophores were collected and processed using Adobe Photoshop. Bar, 15 μm. (B) This triple montage of a series of optical sections was arranged in a similar way to that of A, but in this case the parietal cells were stained with IQGAP2 and F-actin. It was readily apparent, although F-actin is chiefly localized to the apical plasma membranes, the IQGAP2 labeling is released from the apical vacuoles and diffused throughout the cytoplasm. Bar, 15 μm. (C) This triple montage of a series of optical sections was arranged in a similar way to that of A, but in this case the parietal cells were stained with ezrin and F-actin. It was readily apparent, both ezrin and F-actin remain localized to the apical plasma membranes. Bar, 15 μm. (D) The IQGAP-derived peptide increases the extractable Cdc42 and IQGAP2. Cultured parietal cells were treated with the IQGAP-derived peptide followed by a Triton X-100 extraction. The glandular proteins were separated into a soluble and insoluble fraction as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Samples were run on SDS-PAGE, blotted to nitrocellulose, and immunoprobed for ezrin, Cdc42, IQGAP1, and IQGAP2, respectively. The signals were quantified using a PhosphorImager with values expressed as percentage of total (soluble + insoluble). Error bars represent SE; n = 4. Significant difference with respect to the controls (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.05).