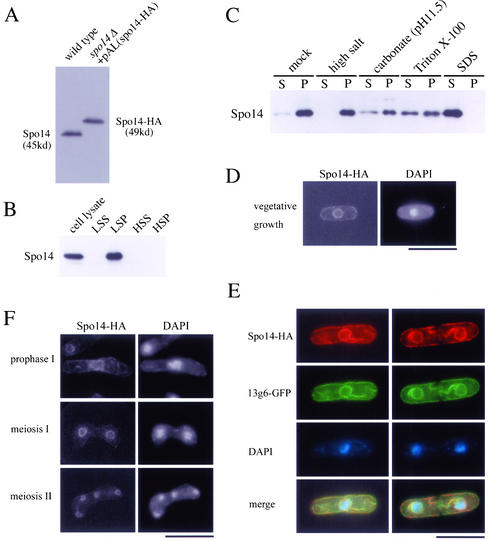
Figure 2.
Localization of Spo14 to the ER membrane. (A) Western blot analysis of S. pombe cell extracts using anti-Spo14 antibody. MKW5 (wild-type) and MK14H (spo14Δ+ pAL(spo14-HA)) cells were grown in liquid complete medium (YE). Protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the anti-Spo14 antibody. (B) Subcellular fractionation of membranes. MKW5 cells were spheroplasted and homogenated. The cell lysates was subjected to differential centrifugation to separate LSP, HSP, and HSS fractions as described in Elagoz et al. (1999). Each fraction was resolved on SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis using anti-Spo14 antibody. (C) The LSP fraction was extracted with lysis buffer (mock) or the same buffer containing either 0.5 M NaCl (high salt), 0.1 M sodium carbonate (pH 11.5), 1.5% Triton X-100, or 0.1% SDS. After extraction, mixtures were fractionated into the supernatant (S) and the pellet (P) by centrifugation (100,000 × g, 1 h). Each fraction was analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Spo14 antibody. (D) Localization of Spo14-HA in vegetative cells. Strain MK14H was cultured in MM medium and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy with anti-HA mAb (3F10) followed by Alexa 488-conjugated anti-rat IgG antibody. Bar, 10 μm. (E) Colocalization of Spo14-HA with an ER marker protein, 13g6. A wild-type strain TN29 carrying pAU(Spo14-HA) and pREP81(13g6-GFP) was grown to midlog phase in MM at 28°C. After fixation, cells were stained with anti-HA antibody (3F10) followed by Alexa 594-conjugated anti-rat IgG antibody and DAPI. Bar, 10 μm. (F) Localization of Spo14 during meiosis. Strain MK14H carrying pAL(spo14-HA) was cultured in SSL−N to induce meiosis. Spo14-HA was visualized as described in Figure 2D. Bar, 10 μm.