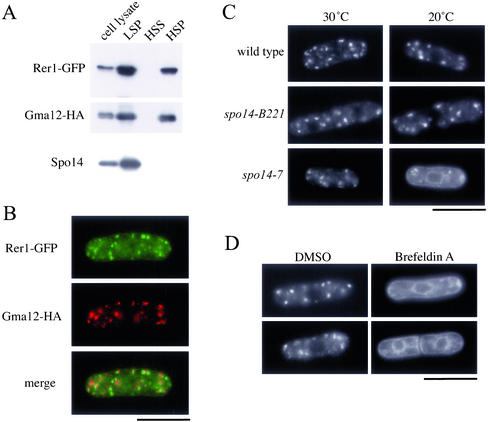
Figure 4.
Effect of the spo14-7 mutation on the ER/Golgi shuttling protein, Rer1. (A) Subcellular fractionation of Rer1-GFP. Strain TN230 transformed with pREP1(gma12-HA) was cultured in MM supplemented with thiamine (20 μM) at 28°C. Cells were converted to spheroplasts, homogenized, and subjected to differential centrifugation to fractionate into LSP, HSP, and HSS. Each fraction was resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis using either anti-GFP, anti-HA, or anti-Spo14 antibody to detect Rer1-GFP, Gma12-HA, and Spo14, respectively. (B) Double-immunofluorescence staining of Rer1 and Gma12. Strain TN230 transformed with pREP1(gma12-HA) was cultured in MM minimal medium supplemented with thiamine (20 μM) at 28°C. Cells were then stained with anti-HA antibody followed by Alexa 594–conjugated anti-rat IgG antibody and DAPI. Bar, 10 μm. (C) ER-to-Golgi transport was blocked in spo14-7. TN52 (wild-type), B221 (spo14-B221), and RM14-7 (spo14-7) cells were transformed with pKB282(rer1-GFP). These strains were grown in liquid medium (MM) at 20°C for 3 h. Localization of Rer1-GFP was observed under a fluorescence microscope. Bar, 10 μm. (D) Effect of Brefeldin A on the localization of Rer1-GFP. Strain TN226 (wild-type) was incubated in MM medium to log phase. Brefeldin A dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was added to the culture medium to a final concentration of 100 μg/ml. After incubation for 2 h, Rer1-GFP was observed under a fluorescence microscope. Bar, 10 μm.