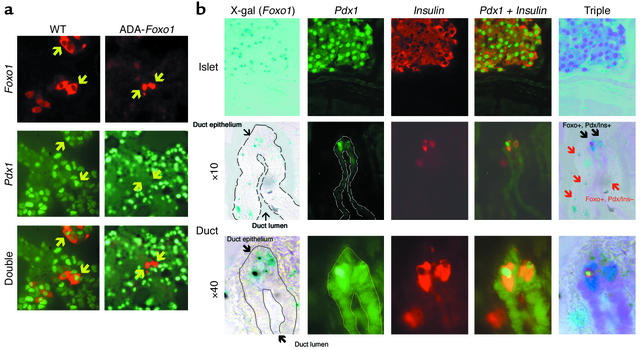
Figure 5.
(a) Pdx1 expression in βTC-3 cells transfected with c-Myc–tagged wild-type (left column) or ADA-Foxo1 (right column). We performed immunocytochemistry with anti–c-Myc (top row) and anti-Pdx1 (middle row). We visualized anti–c-Myc immunoreactivity with CY3-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (red) and anti-Pdx1 immunoreactivity with FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (green). We show double staining in the bottom row. (b) Foxo1 localization in pancreatic duct–associated cells. We treated frozen sections for immunohistochemistry with anti-insulin and anti-Pdx1 antisera, followed by incubation in X-gal to detect β-gal expression from the Foxo1 locus. In the top row, we show a representative endocrine islet, demonstrating that X-gal reactivity colocalizes with islets. Occasional X-gal–positive cells can also be visualized in ducts and acini. In the middle and bottom rows, we show that X-gal reactivity in ducts can be detected in cells that do not express insulin and/or Pdx1 (red arrows), as well as cells with insulin and Pdx1 immunoreactivity (black arrows).