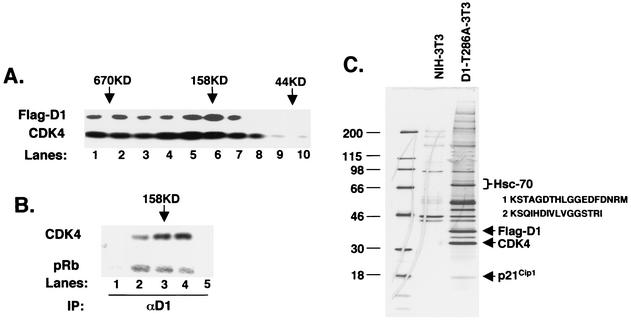
FIG. 1.
Hsc70 copurifies with cyclin D1. (A) Lysates were fractionated by gel filtration chromatography, and 5% of each fraction was resolved by SDS-PAGE; elution of cyclin D1 (top panel) and CDK4 (bottom panel) was visualized by immunoblot analysis. The positions of eluting molecular weight standards are indicated at the top. (B) Fractions corresponding to lanes 4 to 8 in panel A were immunoprecipitated (IP) with a monoclonal antibody specific for cyclin D1 and either blotted for associated CDK4 (top) or assayed for their ability to phosphorylate recombinant GST-Rb (bottom). (C) Detection of cyclin D1 and cyclin D1-associated proteins by silver stain. Lane 1 contains molecular weight markers (sizes shown in kilodaltons), lane 2 contains proteins that nonspecifically bind to M2 beads from control NIH 3T3 lysates, and lane 3 contains cyclin D1 complexes isolated from FlagD1-T286A-3T3 lysates (an essentially identical pattern was recovered from Flag-D1-3T3 cells; data not shown). Proteins were eluted with excess Flag peptide. Positions of Flag-D1, CDK4, and p21Cip1 are indicated to the right, as is the position of Hsc70, along with peptides identified by mass spectrometry.