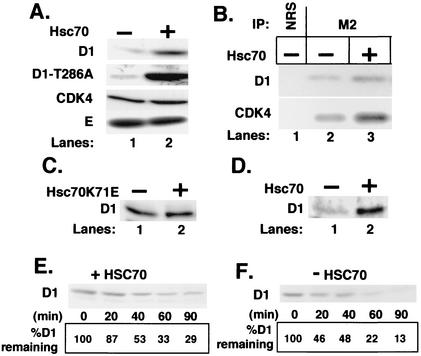
FIG. 4.
Hsc70 decreases cyclin D1 proteolysis. (A) NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with (lane 2) or without (lane 1) a vector encoding Hsc70 along with vectors encoding either cyclin D1 and CDK4 (top and bottom panels), cyclin D1-T286A and CDK4 (second panel), or Myc-tagged cyclin E and CDK2 (bottom panel). Levels of the indicated proteins were determined by direct Western blot analysis of total cell lysates prepared from cells transfected with the indicated vectors. (B) Whole-cell extracts were prepared from NIH 3T3 cells cotransfected with either Flag-D1 and CDK4 (lanes 1 and 2) or Flag-D1, CDK4, and Hsc70 and precipitated with either normal rabbit serum (lane 1) or the M2 monoclonal antibody (lanes 2 and 3). Cyclin D1 and coprecipitating CDK4 were detected by immunoblot analysis with antigen-specific antibodies. (C) NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with a plasmid encoding cyclin D1 with (lane 2) or without (lane 1) a vector encoding Hsc70K71E. Levels of cyclin D1 were monitored by immunoblot analysis. (D) p21/p27−/− MEFs were transfected with a plasmid encoding cyclin D1 without (lane 1) or with (lane 2) a plasmid encoding Hsc70. Levels of cyclin D1 were monitored by immunoblot analysis. (E and F) NIH 3T3 cells transfected with vectors encoding either Flag-D1 and CDK4 or Flag-D1, CDK4, and Hsc70 were treated with 50 μg of cycloheximide per ml, and lysates prepared from these cells at the intervals indicated at the bottom of each panel were subjected to immunoblot analysis for cyclin D1. The percentage of cyclin D1 remaining at each time point is indicated at the bottom of each lane.