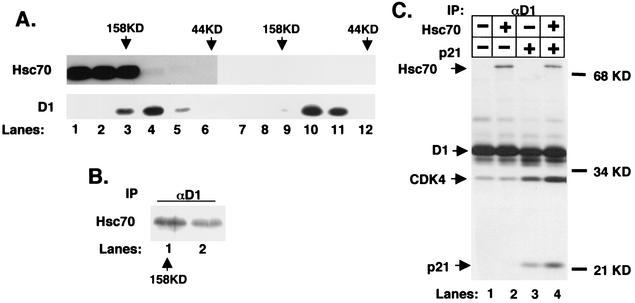
FIG. 5.
Reconstitution of a 158-kDa cyclin-CDK complex. (A) Sf9 insect cells were infected with baculoviruses encoding cyclin D1, CDK4, and p21Cip1 with (lanes 1 to 6) or without (lanes 7 to 12) Hsc70. Lysates prepared from these cells were resolved by gel filtration chromatography and subjected to immunoblot analysis for Hsc70 (top panel) or cyclin D1 (bottom panel). The elution positions of molecular weight standards are indicated at the top of each panel. (B) Fractions corresponding to lanes 3 and 4 of part A were precipitated with the cyclin D1 monoclonal antibody. Coprecipitation of Hsc70 was monitored by immunoblotting with the Hsc70 monoclonal antibody. (C) Lysates prepared from Sf9 insect cells infected with baculoviruses encoding either cyclin D1 and CDK4 (lane 1), cyclin D1, CDK4, and Hsc70 (lane 2), cyclin D1, CDK4, and p21Cip1 (lane 3), or all four (lane 4) and metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine were precipitated with the cyclin D1 monoclonal antibody. Positions of Hsc70, cyclin D1, CDK4, and p21Cip1 are indicated to the left of the panel and were verified independently by immunoprecipitation with antigen-specific antibodies (data not shown). Labeled proteins were visualized by autoradiography.