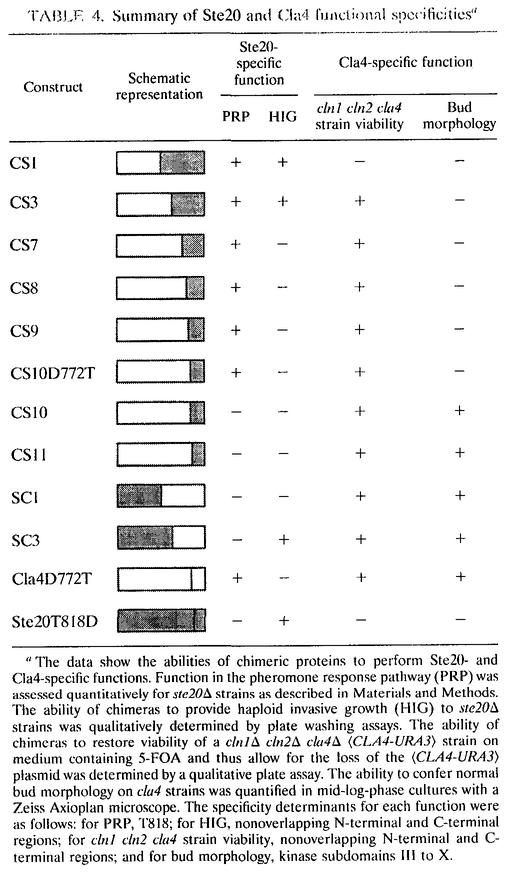
TABLE 4.
Summary of Ste20 and Cla4 functional specificitiesa
The data show the abilities of chimeric proteins to perform Ste20- and Cla4-specific functions. Function in the pheromone response pathway (PRP) was assessed quantitatively for ste20Δ strains as described in Materials and Methods. The ability of chimeras to provide haploid invasive growth (HIG) to ste20Δ strains was qualitatively determined by plate washing assays. The ability of chimeras to restore viability of a cln1Δ cln2Δ cla4Δ 〈CLA4-URA3〉 strain on medium containing 5-FOA and thus allow for the loss of the 〈CLA4-URA3〉 plasmid was determined by a qualitative plate assay. The ability to confer normal bud morphology on cla4 strains was quantified in mid-log-phase cultures with a Zeiss Axioplan microscope. The specificity determinants for each function were as follows: for PRP, T818; for HIG, nonoverlapping N-terminal and C-terminal regions; for cln1 cln2 cla4 strain viability, nonoverlapping N-terminal and C-terminal regions; and for bud morphology, kinase subdomains III to X.