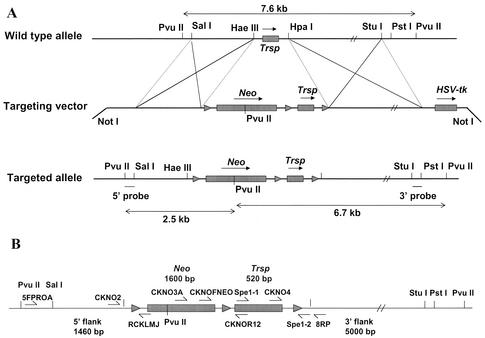
FIG. 1.
Targeting vector, targeted allele, and screening strategy used in generating the conditional knockout of Trsp. (A) Map showing the wild-type allele (upper portion of panel A) encoding Trsp and the restriction sites used in generating the targeting vector (center portion of panel A) that encodes Neo (with its PvuII restriction site, which is critical in distinguishing between the wild-type and target alleles [see below and text]), and Trsp flanked by loxP sites (designated by ▸), herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV-tk), and the NotI restriction sites used in constructing this vector, and the targeted allele (lower portion of panel A) encoding Trsp and Neo flanked by loxP sites (designated by ▸) and the restriction sites used in constructing this allele, in identifying homologous recombination and in distinguishing wild-type and targeted alleles (see text) are presented. Sizes of fragments generated from the wild-type allele (see top of panel A) and targeted allele (see bottom of panel A) by PvuII digestion are also shown. (B) Primers used in identifying the insertion or generation of different regions during construction of the targeting vector and in determining the presence of different regions involved in generating the targeted allele and floxed Trsp and/or Neo are shown along with the sizes of each region cloned into the targeting vector. Maps in panels A and B are not drawn to scale.