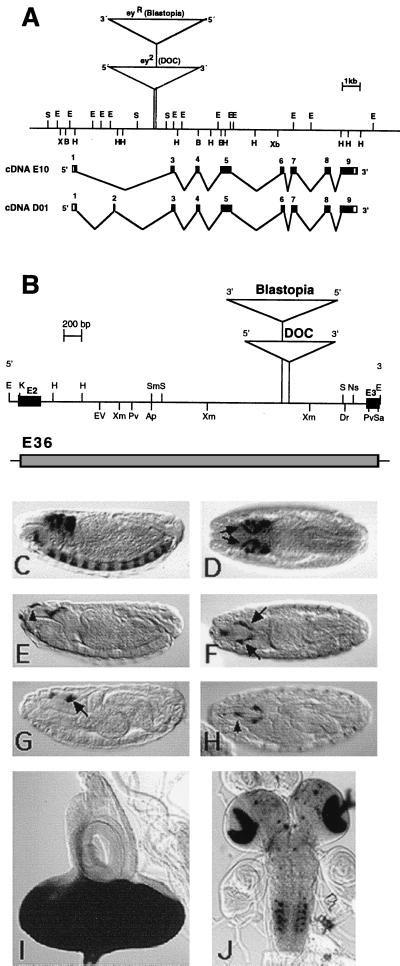
Figure 1.
(A) Genomic organization of the ey gene in D. melanogaster. The restriction map contains the insertion sites of the transposons in the alleles ey2 and eyR shown as triangles. Black boxes indicate exons of the cDNA E10 and D01, respectively. (B) Restriction map of the 3.6-kb EcoRI fragment containing the enhancer harboring intron of the ey gene. ey exon 2 (E2) and exon 3 (E3) are shown as black boxes; triangles indicate the transposon insertion sites in the alleles ey2 and eyR. Shown is expression of the eyeless+ gene in comparison with expression of reporter construct E36. (C and D) In situ hybridization of stage 15 embryos with a DIG-labeled ey probe. (C) Lateral view. (D) Dorsal view. ey is expressed in the brain, the ventral nerve cord, and the eye-antennal disc precursor cells (arrows). The 3.5-kb KpnI fragment that was used in the construct E36 is shown as a shaded box. Expression of reporter construct E36 in embryos (E–H) and larvae (I and J). Anti β-gal staining of stage 15 (E and F) and stage 17 (G and H) embryos shows expression in the eye-antennal disc precursor cells (arrows). The reporter construct shows additional expression in the region of the dorsal pouch (arrowheads). β-gal activity staining of third instar larvae shows strong signal in the eye imaginal disc (I) and a stripe in the antennal disc, in the optic lobes of the brain, and in spots in the ventral ganglion (J). In C–H, anterior is to the left. Staging is according to Campos-Ortega and Hartenstein (30). Ap, ApaI; B, BamHI; Dr, DraI; E, EcoRI; EV, EcoRV; H, HindIII; K, KpnI; Pv, PvuII; S, SalI; Sa, SacI; Sm, SmaI; Xb, XbaI; Xm, XmnI.