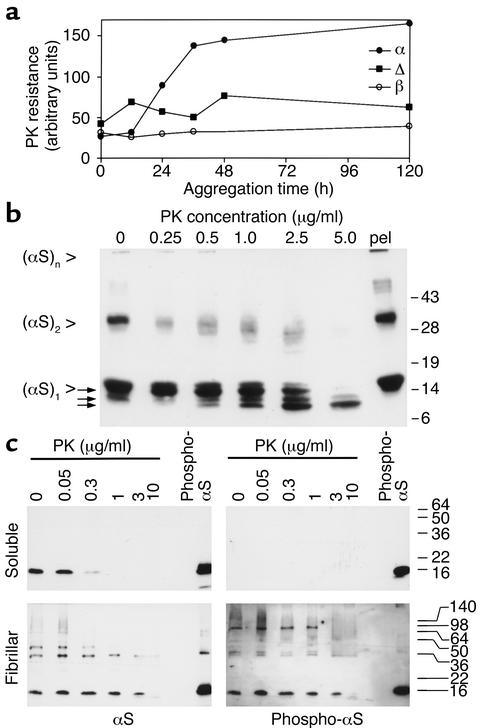
Figure 1.
αS becomes PK-resistant upon aggregation in vitro. (a) Two milligrams per milliliter [wt]αS (filled circles), [Δ73-83]αS (filled squares), and [wt]βS (open circles) were incubated for the indicated times, at which 5-μl samples were taken and treated with PK. Western blots were probed with MC42 to detect [wt]αS and [Δ73-83]αS, and antiserum 6485 to detect [wt]βS. Band signals were quantitated by densitometric scanning. (b) Two milligrams per milliliter [wt]αS were aggregated for 7 days, then digested with the indicated amount of PK, or pelleted by ultracentrifugation (pel). Arrows point to fragments liberated from full-length αS (see text for details). Western blot was probed with 3400 anti-αS. (c) Tissue from a DLB patient was extracted, and the soluble (upper panels) and fibril-containing (lower panels) fractions were digested with the indicated concentrations of PK. Western blots were sequentially probed with phosphospecific anti-αS (right panels) and 15G7 anti-αS (left panels). Exposure times of the blots were chosen to match the intensities of the standard bands (20 ng in vitro–phosphorylated recombinant αS). The experiments were repeated with the same results.