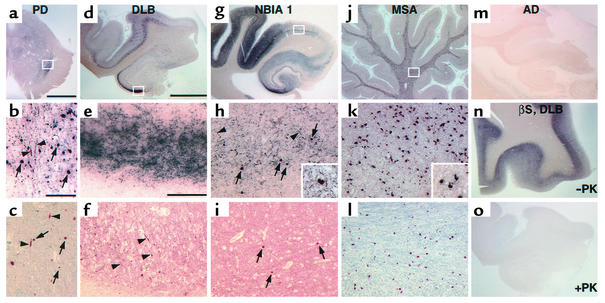
Figure 2.
PK-PET blots and immunohistochemistry in human α-synucleinopathies. (a–l) Representative brain sections from (a–c) PD, (d–f) DLB, (g–i) NBIA1, and (j–l) MSA patients. PK-resistant αS was found on PK-PET blots of PD SN (a) as well as hippocampus and temporal cortex in DLB (d) and NBIA1 (g) brains. (b, e, and h) Higher magnification of the regions boxed in a, d, and g, respectively, shows several LBs (arrows; inset in h), as does standard anti-αS immunohistochemistry of adjacent sections (c, f, and i). In contrast, many more LNs (arrowheads) were observed on PK-PET blots (b, e, and h) than on standard sections (c, f, and i). (j) PK-resistant αS was also detected in cerebellar white matter of MSA patients. (k) Higher magnification of the area boxed in j demonstrates PK-resistant αS in glial cytoplasmic inclusions (inset in k), as confirmed by standard αS immunohistochemistry of an adjacent section (l). (m) No staining was noted on PK-PET blots in the hippocampal formation of Alzheimer disease (AD) patients. (n and o) Antibody against βS in a DLB case shows an intense staining only without PK digest (n), whereas virtually no staining remained after PK treatment (o). Scale bar in a, 5 mm; in b, 200 μm (b and c); in d, 5 mm (d, g, j, and m–o); in e, 200 μm (e, f, h, i, k, and l).