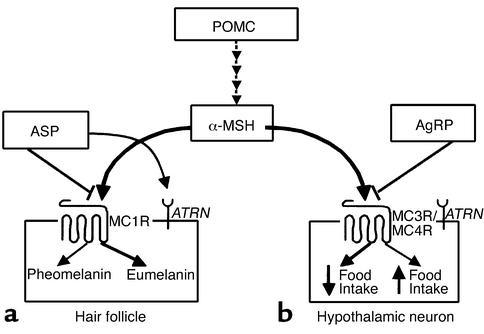
Figure 1.
Schematic of melanocortin-signaling pathways, specifically melanocortin signaling in the hair follicle and hypothalamus. α-MSH is a melanocortin peptide that is cleaved from the pro-opiomelanocortin precursor (POMC). (a) α-MSH acts on MC1R, resulting in an increase in cAMP to darken coat color. ASP antagonizes α-MSH binding at MC1R, resulting in pheomelanin synthesis. ATRN (mahogany) may function to downregulate or desensitize MC1R or may be involved in ASP processing or binding to MC1R. (b) α-MSH activates MC4R to decrease food intake and increase energy expenditure. AgRP competes with α-MSH for binding at MC4R/MC3R, resulting in increased food intake. Ay mice ectopically overproduce ASP, interfering with α-MSH signaling at MC4R/MC3R and resulting in an obese phenotype due to increased food intake.