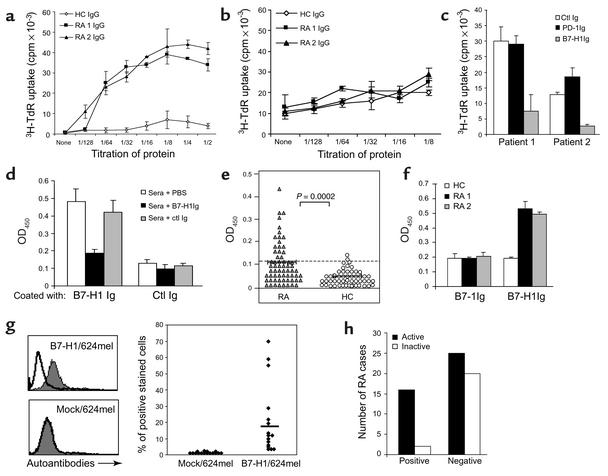
Figure 1.
Detection, costimulatory function, and disease association of B7-H1 autoantibodies in RA patients. CD4+ T cells were cultured with immobilized (a) or soluble (b) sera IgG at the initiated dose of 20 μg/ml in the presence of suboptimal anti-CD3 mAb. The titers of RA 1 and RA 2 patients are 0.32 and 0.25 (OD450), respectively. (c) For blockade, the control (ctl) Ig, PD-1Ig, or B7-H1Ig at 3 μg/ml were added before the addition of CD4+ T cells. The growth of T cells was detected after 72 hours of culture. (d) To examine specificity of RA sera binding to B7-H1, diluted sera were preincubated with PBS, 2 μg/ml of soluble B7-H1Ig or control Ig (mIgG2a). (e) Diluted sera of 63 patients with RA and 54 healthy donors were tested for binding to B7-H1Ig by ELISA. Samples with OD450 values greater than 0.123 were considered positive. P value for differences between cohorts is shown (t test). (f) The sera at 1:1,000 dilution were examined for binding to B7-1Ig–coated vs. B7-H1Ig–coated ELISA plates. (g) Mock/624mel or B7-H1/624mel cells were stained with diluted (1:5) sera from 16 ELISA-positive RA patients. The inset bar shows the average percentage of positive staining. A typical histogram of FACS assay is shown on the left. (h) Sixty-three RA patients were sorted according to the active status of their disease, and the presence of B7-H1 autoantibodies. Statistical analysis of the correlation was performed as P = 0.0179 in a Fisher exact test.