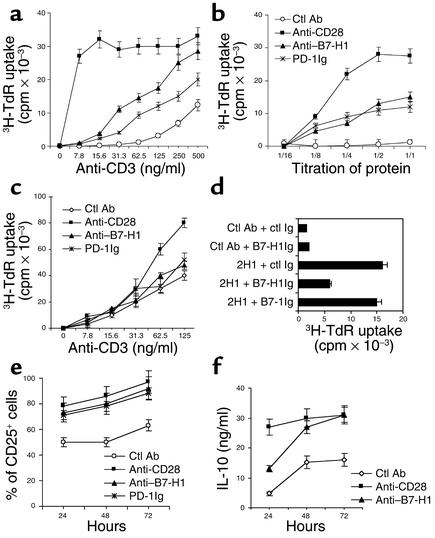
Figure 3.
B7-H1 mAb costimulates human CD4+ T cell proliferation. (a) Purified human CD4+ T cells were cultured with immobilized 10 μg/ml of control (ctl) Ab, B7-H1 mAb (2H1), PD-1Ig, and 2 μg/ml of CD28 mAb in the presence of precoated different dose of CD3 mAb. Cultures were pulsed with 3H-TdR for a final 16 hours, and the cells were harvested at 72 hours. (b) Dose-dependent costimulation of immobilized anti–B7-H1 mAb in the presence of suboptimal dose (30 ng/ml) of CD3 mAb. Titration of mAb or fusion protein was started at 20 μg/ml of control Ab, B7-H1 mAb, PD-1Ig, and 4 μg/ml of CD28 mAb. (c) Human CD4+ T cells were costimulated with 20 μg/ml of soluble control (ctl) Ab, B7-H1 mAb (2H1), PD-1Ig, and 2 μg/ml of CD28 mAb as the same condition in a. (d) Blocking of B7-H1 mAb–mediated costimulation by soluble B7-H1Ig. Soluble control Ig, B7-1Ig, or B7-H1Ig (10 μg/ml) was preincubated with immobilized control (ctl) Ab or B7-H1 mAb (2H1) for 30 minutes before the addition of T cells. B7-H1 costimulation was assayed in the presence of suboptimal dose of CD3 mAb for 72 hours of culture. (e) FACS analysis of IL-2 receptor (CD25) expression in CD4+ T cells after B7-H1 mAb costimulation. (f) IL-10 secretion from CD4+ T cells in the presence of immobilized CD3 mAb (500 ng/ml), and B7-H1 mAb (10 μg/ml), or CD28 mAb (2 μg/ml).