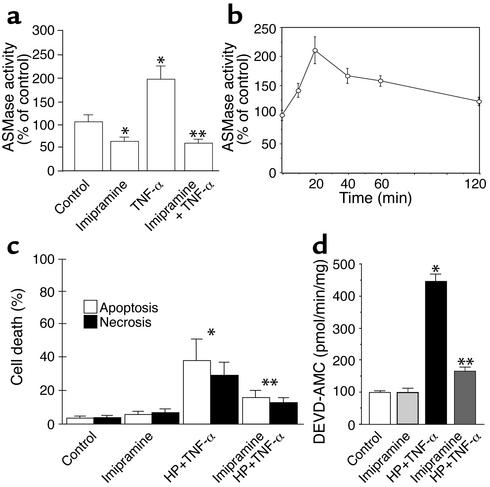
Figure 3.
Imipramine inactivates ASMase in hepatocytes. (a) Hepatocytes were treated with TNF-α (280 ng/ml) for 2 hours with or without preincubation with imipramine (50 μM). Cellular extracts were used for ASMase activity determined from N-methyl-[14C]sphingomyelin (56.6 mCi/mmol) hydrolysis. Levels of phosphorylcholine produced from sphingomyelin were determined in the aqueous phase by scintillation counting. Results are expressed as means ± SD (n = 5 independent experiments). *P < 0.05 versus control, and **P < 0.05 versus TNF-α. (b) The activity of ASMase with or without imipramine pretreatment was determined at different times after TNF-α exposure as in a. (c) To test the role of imipramine in cell survival, hepatocytes were first treated with HP and then incubated with TNF-α (280 ng/ml) for 12 hours. Cell death was determined by Hoechst 33258 and propidium iodide staining. Results are expressed as means ± SD (n = 4 independent experiments). *P < 0.05 versus control, and **P < 0.05 versus HP plus TNF-α. (d) The activity of caspase 3 was determined under these various conditions with or without imipramine preincubation from the fluorescence of released AMC fragments. Results are expressed as means ± SD (n = 4 independent experiments). *P < 0.05 versus control, and **P < 0.05 versus HP plus TNF-α.