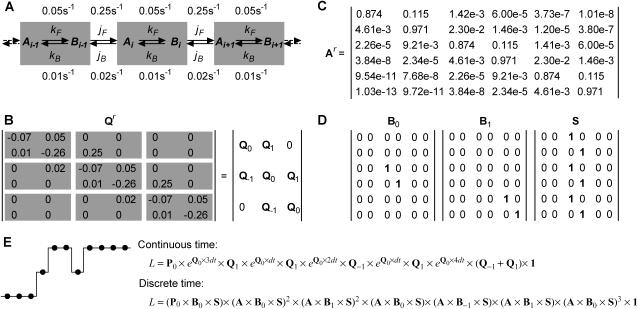
FIGURE 2.
Molecular motors can be represented with reduced Markov models. (A) The mechano-chemistry of molecular motors is a repetitive chain of identical reaction units. Each unit includes the conformations assumed by the protein while located at a given position along the cytoskeleton. The example shown is for a model with two states per reaction unit. Only transitions between states within different units can be detected experimentally. (B) The rate matrix Q of the Markov model is block tridiagonal and periodic. Shown is a submatrix Qr copied from the theoretically infinite Q, and its block representation. Note that the first and last rows are not zero-sum. (C) A truncated transition probability matrix Ar is calculated as 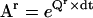 . The example is shown for a sampling interval dt = 0.5 s. Note that Ar is also periodic. (D) Auxiliary matrices (Bi and S) used in the calculation of the discrete-time likelihood function. (E) An example of likelihood calculation, for either the continuous-time or the discrete-time Markov model (see text for details).
. The example is shown for a sampling interval dt = 0.5 s. Note that Ar is also periodic. (D) Auxiliary matrices (Bi and S) used in the calculation of the discrete-time likelihood function. (E) An example of likelihood calculation, for either the continuous-time or the discrete-time Markov model (see text for details).