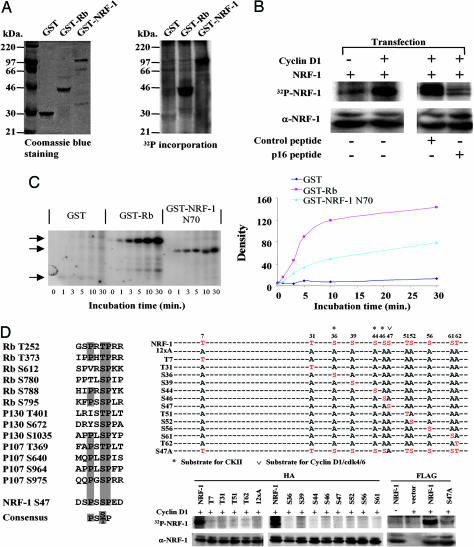
Fig. 4.
NRF-1 serves as substrate of cyclin D1-dependent kinase. (A) GST-NRF-1 was incubated with immunoprecipitated cyclin D1/Cdk4 kinase complex in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. (A Left) Coomassie blue staining of input GST protein. (A Right) γ-32P incorporation into GST-NRF-1. GST and GST-RB were negative and positive control for kinase activity. (B Left) HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-NRF-1 with cyclin D1 or control empty vector. (B Right) HEK293T cells transfected with FLAG-NRF-1 and cyclin D1 were treated with p16INK4a peptide (20 μM) corresponding to amino acids 84–103 of the human p16INK4a protein (DAAREGFLATLVVLHRAGAR) with a C-terminal 16-aa Penetratin (RQIKIWFQNRRMKWKK) or control peptide (Biosynthesis, Lewisville, TX) (16). NRF-1 phosphorylation was abrogated by p16INK4a peptide. Cells were pulse-labeled with [γ-32P]orthophosphate. NRF-1 protein was precipitated with anti-FLAG M2 antibody and subjected to autoradiography. (C Left) Equal amounts of either the GST-NRF-1 N70 fusion protein or GST protein were incubated with 200 ng of purified cyclin D1/Cdk4 complex and [γ32P]ATP. The arrows indicate the autoradiogram of the phosphorylated fusion protein. (C Right) GST-Rb serves as a positive control. The phosphorylated bands were quantified by densitometry scanning. (D) Alignment of Cdk4 phosphorylation sites for pRb, p107, p130, and NRF-1. HEK293T cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding hemagglutinin or FLAG-tagged NRF-1 and mutants in which a single potential phosphorylation site was restored in all sites mutated version (12xA) or a single point mutant of S47, together with cyclin D1. NRF-1 and mutant protein were precipitated with anti-hemagglutinin antibody and subjected to autoradiography.