Figure 1.
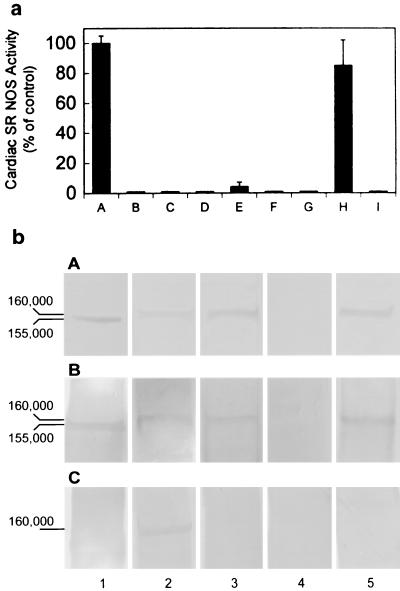
(a) NO synthase activity was found in isolated cardiac SR vesicles. Lane A: control, in the presence of NOS substrates and cofactors: Ca2+, CaM, NADPH, FMN, FAD, [3H]arginine, and BH4; lane B: in the presence of NOS substrates without vesicles; lane C: boiled vesicles + NOS substrates and cofactors; lane D: in the absence of Ca2+; lane E: with EGTA and NOS substrates and cofactors; lane F: with 10 μM 7-NI; lane G: with 60 μM TRIM; lane H: with 10 nM AMT; and lane I: iNOS in the presence of 10 nM AMT. These results demonstrate that SR NOS activity is Ca2+ dependent and is sensitive to nNOS selective inhibitors, indicating the existence of NOS in cardiac SR vesicles and the specificity of a neuronal-type NOS enzymatic activity. The data represent a mean of six independent experiments. (b) Western blot analysis of cardiac SR NOS. Cardiac SR vesicles were fractionated by electrophoresis through a 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and transferred to nitrocellulose. Incubated with Affinity BioReagents anti-nNOS antibody (bA), with anti-nNOSα antibody (bB), and with anti-nNOSμ antibody (bC). Column 1: rat brain homogenate; 2: mice heart homogenate; 3: mice cardiac SR vesicles; 4: nNOS knockout mice cardiac SR vesicles; and 5: rabbit cardiac SR vesicles. All of the samples were 30 μg (total protein) per lane. Both rabbit and mice cardiac SR NOS were detected by anti-nNOS and anti-αnNOS antibodies. The results also show that the denatured molecular masses of rat brain NOS and cardiac SR NOS were ≈155 and 160 kDa, respectively.