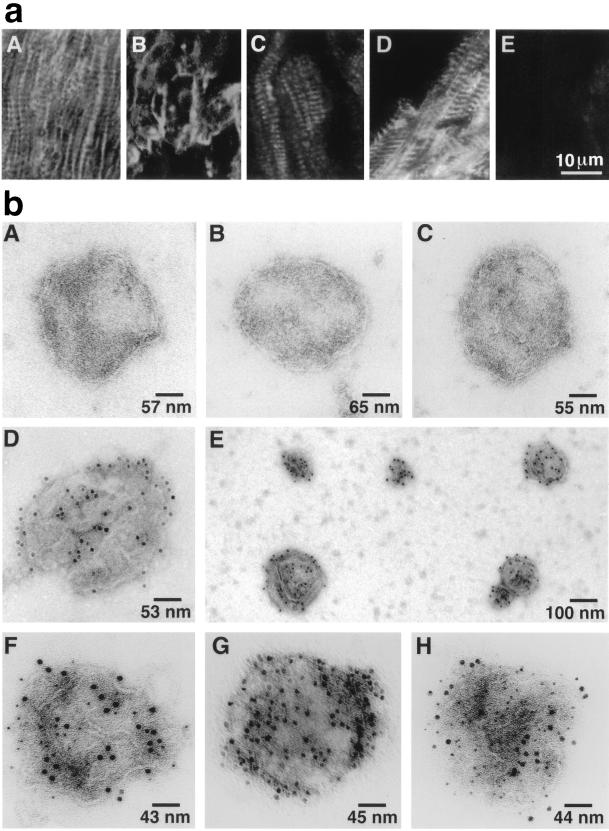
Figure 3.
(a) Immunofluorescent localization of cardiomyocyte antigens with mAbs on cryostat sections of human ventricular myocardium by laser-scanning confocal microscopy. (aA) nNOS indirect immunofluorescent labeling (IIL) shows a linear longitudinal and transverse, striated pattern of labeling; Na+,K+-ATPase IIL demonstrates a distinctly different sarcolemma pattern of labeling of the human heart section (aB); RyR IIL (aC) and SERCA2 IIL (aD) have a similar pattern of labeling as NOS IIL suggesting SR localization of NOS rather than exclusive sarcolemma localization in cardiac muscle; an irrelevant anti-viral protein mAb (aE) used at the same concentration as the other primary mAbs, has only low levels of background fluorescence. (b) Single immunogold labeling. SR vesicles were incubated with specific primary antibodies and a secondary antibody conjugated to 12 nm of colloidalgold. Control vesicles in the absence of primary antibody (bA); with anti-eNOS (bB); with anti-iNOS (bC); and single vesicle (bD) and a group of vesicles (bE) with anti-nNOS. Electron photomicrographs show that only nNOS is broadly dispersed on the surface of cardiac muscle SR membrane vesicles. Double immunogold labeling: Ca2+-ATPase (6 nm gold particles) and nNOS (12 nm) (bF); Na+, K+-ATPase (6 nm) and nNOS (12 nm) (bG); and phospholamban (6 nm) and nNOS (12 nm) (bH). Each vesicle represents hundreds of similar labeled or unlabeled vesicles in each condition. The results show that cardiac SR Ca2+-ATPase and phospholamban coexist with a SR neuronal-type NOS. Absence of Na+,K+-ATPase on the SR vesicles further demonstrates the vesicles represent SR rather than sarcolemma.