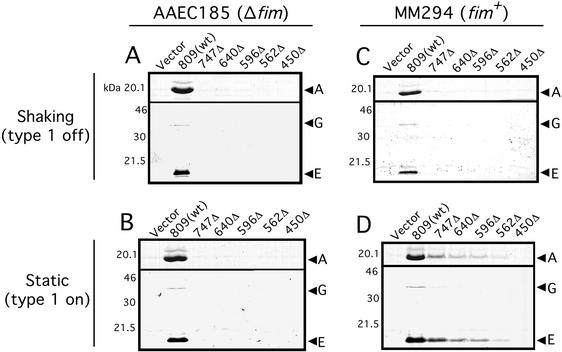
FIG. 7.
Pilus biogenesis by the PapC C-terminal truncation mutants. (A and B) AAEC185 (Δfim)/pMJ2 (ΔpapC pap operon) was transformed with vector alone (pMON6235Δcat), full-length PapC (pMJ3) [809(wt)], or the indicated PapC truncation mutant. Bacteria were grown at 37°C in shaking broth (A) or static broth (B). P pili assembled on the cell surface were harvested by heat extraction and magnesium precipitation, followed by separation on SDS-PAGE. The PapA major rod subunit was visualized by Coomassie blue staining (upper panel in each figure). The PapG adhesin and PapE major tip subunit were visualized by immunoblotting with anti-P pilus tip antibody (lower panel in each figure). The positions of the PapA, PapG, and PapE subunits are indicated. (C and D) P Pili were purified from strain MM294 (fim+)/pMJ2 transformed with the indicated PapC construct as described above. Bacteria were grown in shaking broth (C) or static broth (D). Growth in shaking or static broth represses or induces type 1 pilus expression, respectively.