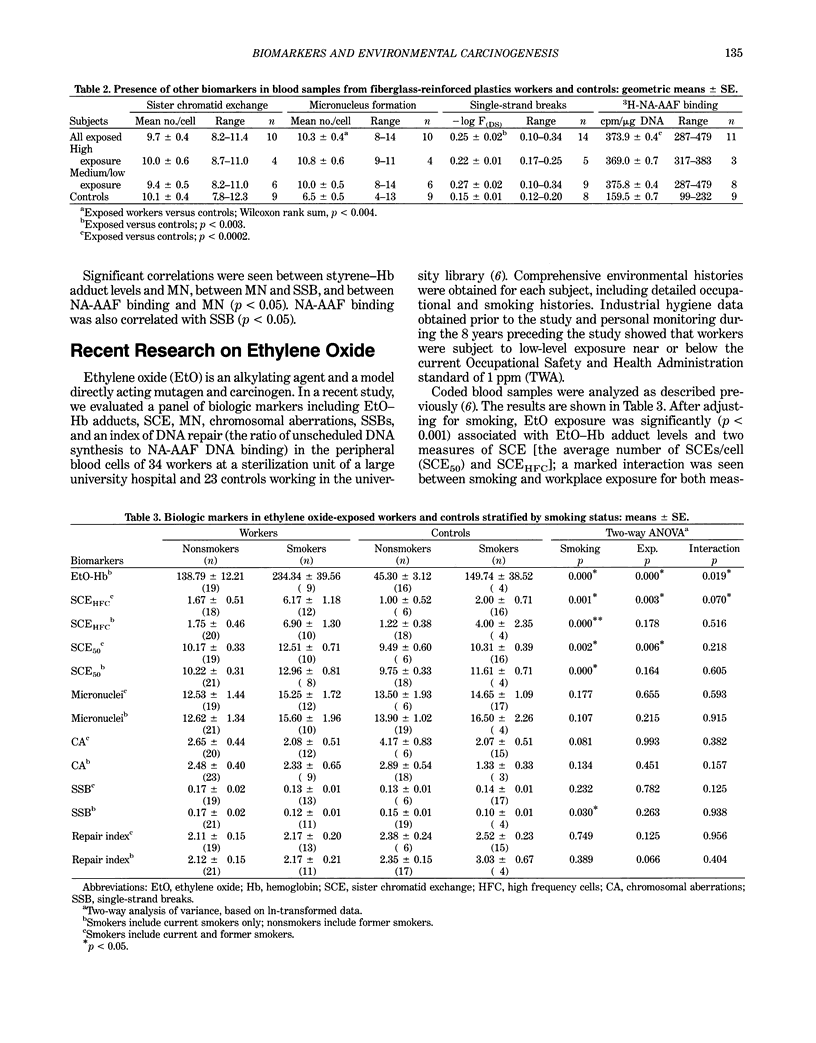
Abstract
Prevention of environmentally related cancer will be enhanced by the availability of sensitive early warning systems and by improvements in quantitative assessment of human risks. Accordingly, we have carried out a series of molecular epidemiologic studies aimed at validating a panel of biologic markers, including carcinogen–DNA and –protein adducts, sister chromatid exchange, micronucleus formation, DNA strand breaks, and DNA repair capacity. Results from three such studies illustrate the usefulness of these biomarkers in elucidating low-dose–response relationships, correlations between biomarkers, and the range of variation in biomarkers between individuals exposed to similar concentrations of carcinogens. Low-level workplace or ambient exposures to styrene, ethylene oxide, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) were associated with significant increases in both molecular dose of carcinogens (adducts) and various markers of preclinical effects. Correlations between biomarkers varied by exposure. For example, in the styrene study, sister chromatid exchange frequency was not correlated with any of the markers, in contrast to the studies of ethylene oxide and PAH. Significant molecular effects were observed not only in occupationally exposed people but also in residents of an area in Poland characterized by high levels of air pollution. For example, the mean PAH–DNA level in exposed residents (winter sample) was 30.4 adducts per 108 nucleotides. This level was significantly higher than that of adducts seen in summer samples from the same area (4.2/108), or in winter samples from residents of a rural area (11.01/108). Significant seasonal variation in PAH–DNA adduct formation in this group was consistent with recorded fluctuations in air pollution levels. Striking interindividual variation was observed in all three exposed populations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. D., Jeffrey A. M., Latriano L., Wazneh L., Warburton D., Toor M., Pero R. W., Andrews L. R., Walles S., Perera F. P. Biomarkers in styrene-exposed boatbuilders. Mutat Res. 1991 Nov;261(3):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(91)90071-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calleman C. J., Ehrenberg L., Jansson B., Osterman-Golkar S., Segerbäck D., Svensson K., Wachtmeister C. A. Monitoring and risk assessment by means of alkyl groups in hemoglobin in persons occupationally exposed to ethylene oxide. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1978 Nov-Dec;2(2):427–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. C. Interindividual variation among humans in carcinogen metabolism, DNA adduct formation and DNA repair. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Sep;10(9):1563–1566. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.9.1563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Försti A., Mustonen R., Savela K. DNA adducts in experimental cancer research. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1986;112(3):181–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00395910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Grzybowska E., Chorazy M., Twardowska-Saucha K., Sroczynski J. W., Putman K. L., Randerath K., Phillips D. H., Hewer A., Santella R. M. DNA adducts in human environmentally exposed to aromatic compounds in an industrial area of Poland. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jul;11(7):1229–1231. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.7.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson J. T., Jones R. D. Mortality of styrene production, polymerization and processing workers at a site in northwest England. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Oct;11(5):347–352. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer J., Warburton D., Jeffrey A. M., Pero R., Walles S., Andrews L., Toor M., Latriano L., Wazneh L., Tang D. Biologic markers in ethylene oxide-exposed workers and controls. Mutat Res. 1991 May;248(1):163–176. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motykiewicz G., Michalska J., Szeliga J., Cimander B. Mutagenic and clastogenic activity of direct-acting components from air pollutants of the Silesian industrial region. Mutat Res. 1988 Feb;204(2):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motykiewicz G., Szeliga J., Cimander B., Choraźy M. Seasonal variations in mutagenic activity of air pollutants at an industrial district of Silesia. Mutat Res. 1989 Jun;223(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(89)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okun A. H., Beaumont J. J., Meinhardt T. J., Crandall M. S. Mortality patterns among styrene-exposed boatbuilders. Am J Ind Med. 1985;8(3):193–205. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700080305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Sittert N. J., de Jong G., Clare M. G., Davies R., Dean B. J., Wren L. J., Wright A. S. Cytogenetic, immunological, and haematological effects in workers in an ethylene oxide manufacturing plant. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Jan;42(1):19–26. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


