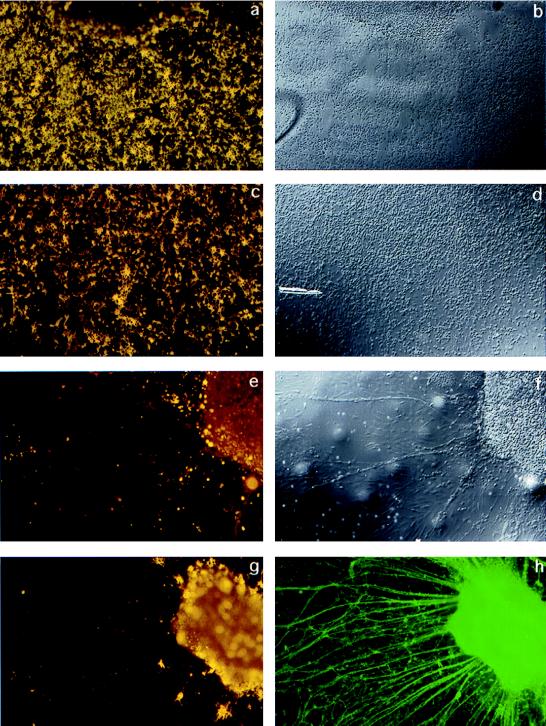
Figure 3.
Neutralizing neuregulin activity inhibits the formation of oligodendrocytes in wild-type spinal cord explant cultures. IgB4 is a chimeric protein consisting of the extracellular domain of erbB4 (ligand-binding domain) and the Fc portion of human IgG1. Spinal cord explants were generated from E9.5 wild-type mice and cultured for 2.5 days in standard growth medium then 9 days in the presence of human Fc fragment as a control (a–d) or IgB4 (e–h). At day 11, cultures were surface stained with mAb O4 and O1 combined to identify immature and mature oligodendrocytes, fixed, and, in some cases, double-labeled with antineurofilament. (a, c, e, g) Combined O4 and O1 staining. b, d, and f are Nomarski images corresponding to a, c, and e, respectively. h shows the neurofilament staining corresponding to g. In cultures treated with IgB4, there are few or no oligodendrocytes identified. In contrast, wild-type explant cultures treated with the control buffer containing human Fc fragment had abundant numbers of oligodendrocytes.