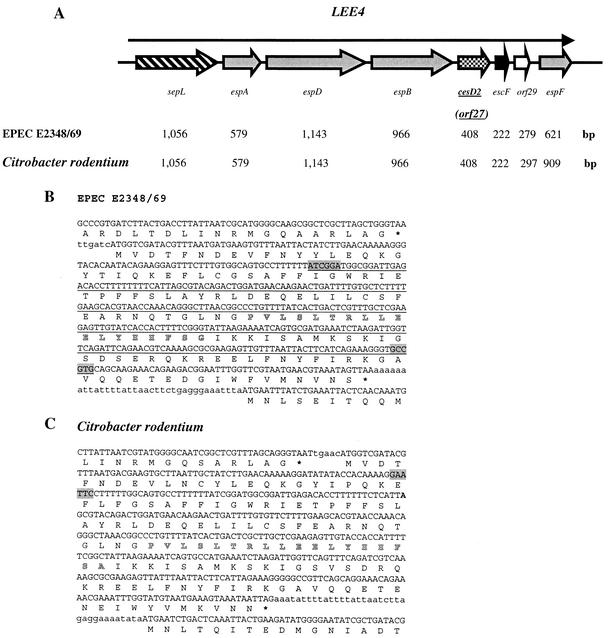
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of LEE4, DNA sequence, and deduced amino acid sequence of cesD2 (formerly orf27). (A) Overview (not to scale) of the organization of the LEE4 operon. Arrows represent each of the open reading frames, with their length indicated below. (B and C) Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of espB (carboxyl-terminal region), cesD2 (orf27), and escF (amino terminal region) from EPEC E2348/69 and C. rodentium. Outlined amino acid sequences indicate a potential amphipathic α-helix in CesD2. (B) The underlined DNA sequence indicates the deletion in EPEC ΔcesD2 and the insertion point of the aphT cassette. Highlighted sequences indicate the points wherein the SmaI sites were introduced for construction of EPEC ΔcesD2::aphT. (C) Highlighted sequence indicates the EcoRI site where the aphT cassette was inserted, creating a C. rodentium strain that is cesD2::aphT.