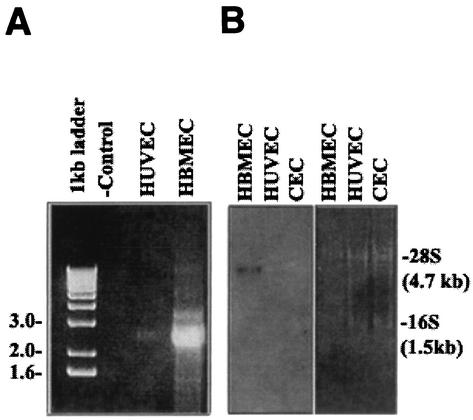
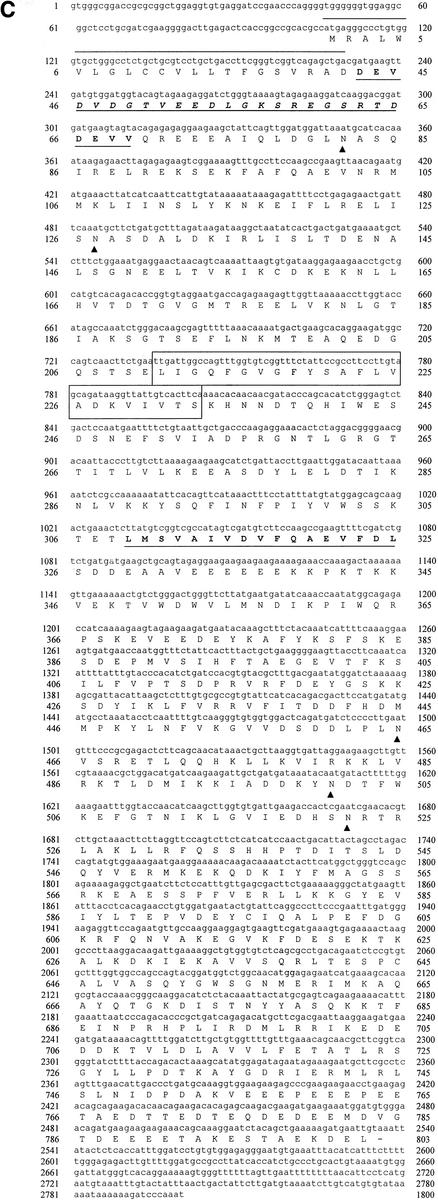
FIG. 2.
Generation of the Ecgp gene by RT-PCR, and the nucleotide sequence of Ecgp. (A) Total RNAs of HBMEC and HUVEC were used to generate an RT-PCR product by using primers generated from the gp96 sequence. HBMEC RNA without primers was used as a negative control (− control). (B) Northern blot analysis of total RNA from HBMEC, HUVEC, and CEC by use of the labeled 7c clone as a probe. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide before transfer to a nylon membrane. Molecular sizes of 28S and 16S RNA are shown on the right. (C) Ecgp nucleotide and derived amino acid sequences obtained from cDNA sequencing and 5′ RACE. The initiation methionine was identified as the first ATG in the open reading frame and obeys Kozak's consensus. A 21-amino-acid putative signal peptide (overlined), potential N-glycosylation sites (triangles), and 23 hydrophobic amino acids representing a putative transmembrane domain (boxed) were found. An endoplasmic retention sequence (KDEL) before the stop codon and a poly(A) tail at the end of the sequence were found. The protein sequences obtained by partial N-terminal amino acid analyses of 95- and 65-kDa proteins in our previous study are boldfaced and underlined.