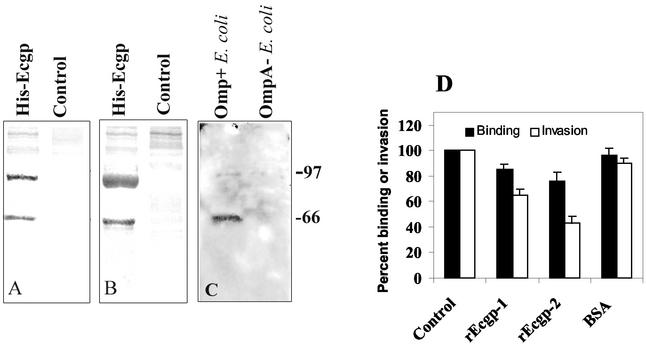
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of OmpA+ E. coli invasion by rEcgp. (A) rEcgp (5 μg) isolated from CHO cells transfected with Ecgp was separated by SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and stained with Coomassie blue. (B) A duplicate gel was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and immunoblotted with an anti-His antibody. (C) Purified rEcgp (10 μg) was incubated with either OmpA+ or OmpA− E. coli for 1 h on ice and washed thoroughly, and bound proteins were released with Laemmli buffer. The proteins, after separation by SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, were immunoblotted with an anti-His antibody. (D) Various concentrations of rEcgp were incubated with OmpA+ E. coli for 1 h on ice prior to addition to HBMEC monolayers. Levels of both total cell-associated bacteria (Binding) and intracellular bacteria (Invasion) were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The experiments were carried out at least twice in triplicate, and results are expressed as percent binding or percent invasion, with the control invasion taken as 100%. Error bars, standard deviations from the means.