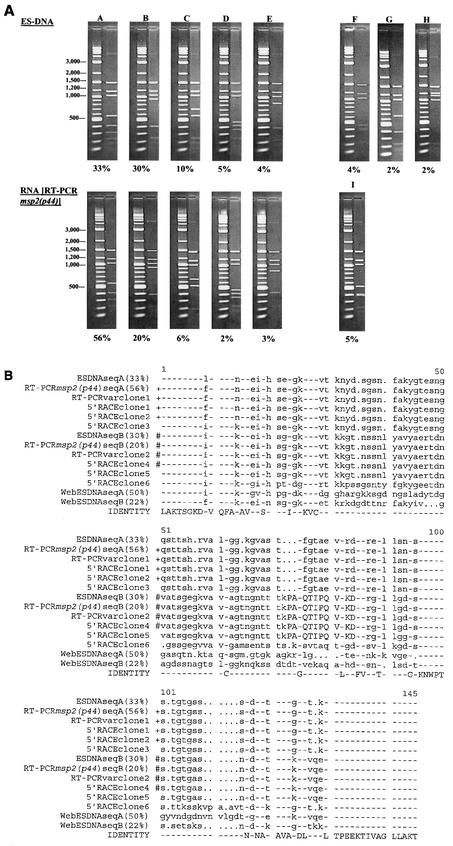
FIG.5.
Sequence diversity in mRNA encoding msp2(p44) reflects polymorphisms in the msp2(p44) copy within the genomic expression site. (A) RFLP analysis of expression site clones compared to RFLP analysis of msp2(p44) mRNA. Plasmid DNAs from 135 independent strain NY18 genomic expression site clones (ES-DNA) and 95 independent clones derived by RT-PCR from NY18 msp2(p44) mRNA were digested with EcoRI and RsaI and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Clones with identical digestion patterns were grouped together, and the frequencies of the major patterns were determined. Each digestion pattern (on the right) is shown next to a marker lane of molecular weight standards. The percentage of clones with each digestion pattern is shown below. Minor patterns representing <2% of the population are not shown; therefore, the sums of the percentages shown are <100%. The predominant variants, represented by clones A through E, have the same digestion patterns whether they are derived from DNA or from RNA. Patterns F through I, representing minor variants, were unique to clones derived from either DNA or RNA. (B) Sequence comparison of genomic expression site clones with clones derived from msp2(p44) mRNA. Individual expression site clones representing the predominant RFLP patterns A and B (Fig. 5A) were sequenced and aligned with the sequences of six 5′-RACE clones and two RT-PCRvar clones, also derived from strain NY18 msp2(p44) mRNA. For comparison, the two predominant genomic expression site sequence variants present in strain Webster (WebESDNAseqA and WebESDNAseqB) are included at the bottom of the alignment. The amino acids encoded by probe 4 (see Fig. 1 and 3), specific for the CVR sequence expressed in strain NY18, are capitalized (amino acids 73 to 84). Identical sequences are indicated by identical symbols (+ or #) to the left of the aligned sequences. Although not identical, the sequences of ESDNAseqA and 5′-RACE clone 5 each differed by only a single amino acid from the two groups of identical sequence variants. These changes could represent actual minor variation in mRNA species or a mutation occurring during in vitro amplification and cloning.