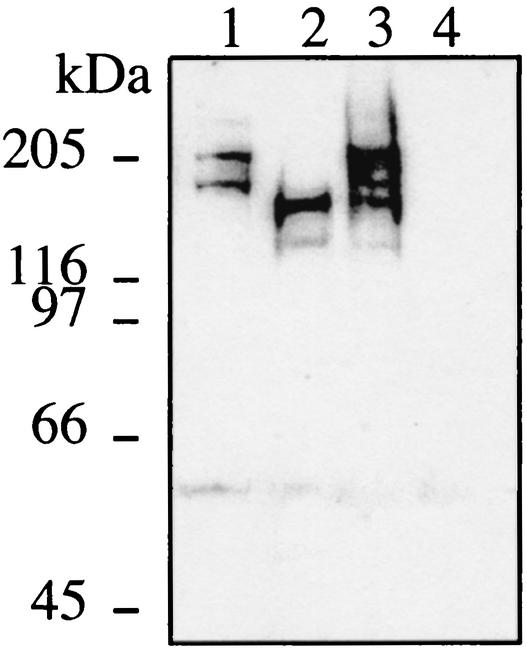
FIG. 2.
Immunodetection of FrpC and FrpC-like proteins in MC58 wild-type and frp mutant strains. Strains were ΔNMB0585 (lane 1), ΔNMB1415 (lane 2), wild-type MC58 (lane 3), and frp double mutant (lane 4). The intermediate band (150 kDa) probably results from proteolytic processing, since meningococcal RTX proteins are known to be highly susceptible to proteolysis (12). A loopful of bacteria, grown overnight on GCB plates, was resuspended in 500 μl of RPMI medium, and 100 μl of this suspension was inoculated in 2 ml of RPMI medium. After 150 min of static culture at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2, 200-μl aliquots were inoculated in 2 ml of RPMI medium, to which the iron chelator desferrioxamine (desferal) was added at a 200 μM final concentration in order to induce the expression of the frp genes. After 2 h, the bacteria were harvested by centrifugation, resuspended in loading buffer containing 8 M urea, boiled for 5 min, and loaded on a sodium dodecyl sulfate-7.5% polyacrylamide gel. After electrotransfer to nitrocellulose membrane, the Frp-derived proteins were detected by using an Frp-specific rabbit serum raised against purified recombinant FrpC (5) and were revealed by enhanced chemiluminescence detection with an anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (Amersham Biosciences).