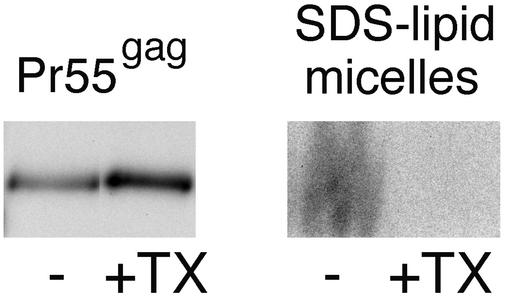
FIG. 4.
Triton X-100 extracts the bulk of envelope phospholipids from the VLP-Pr55gag. VLPs were collected from SFV-C/HIVgag-infected Jurkat cells that had been metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine and [32P]orthophosphate. VLPs were extracted with 1% Triton X-100 at 0°C, and the lysate was fractionated on an iodixanol step gradient as shown in Fig. 1. Buoyant Pr55gag complexes from the 30 to 40% iodixanol interphase were concentrated by ultracentrifugation. The resulting pellet (+TX), as well as an intact, non-Triton X-100-extracted VLP sample (−), were solubilized with hot SDS and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Equivalent amounts of samples were loaded on 10% (Pr55gag) and 20% (SDS-lipid micelles) polyacrylamide gels. On 20% polyacrylamide gels, mixed SDS-lipid micelles separate from other 32P-labeled material. Comparison of the 10 and 20% polyacrylamide gels demonstrates that although the intact VLP and the Triton X-100-treated samples contained similar amounts of Pr55gag complexes, the two samples significantly differed in their phospholipid contents. The radioactive signal in the mixed SDS-lipid micelles originates from both glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin.