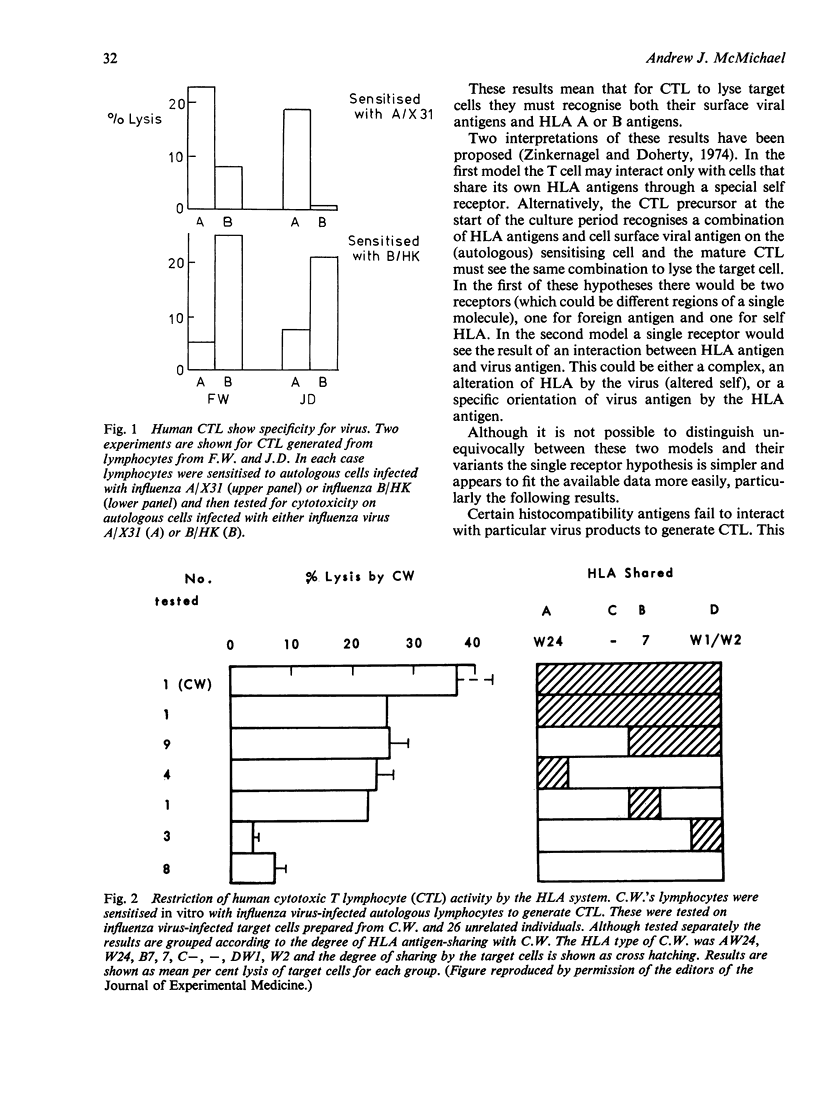
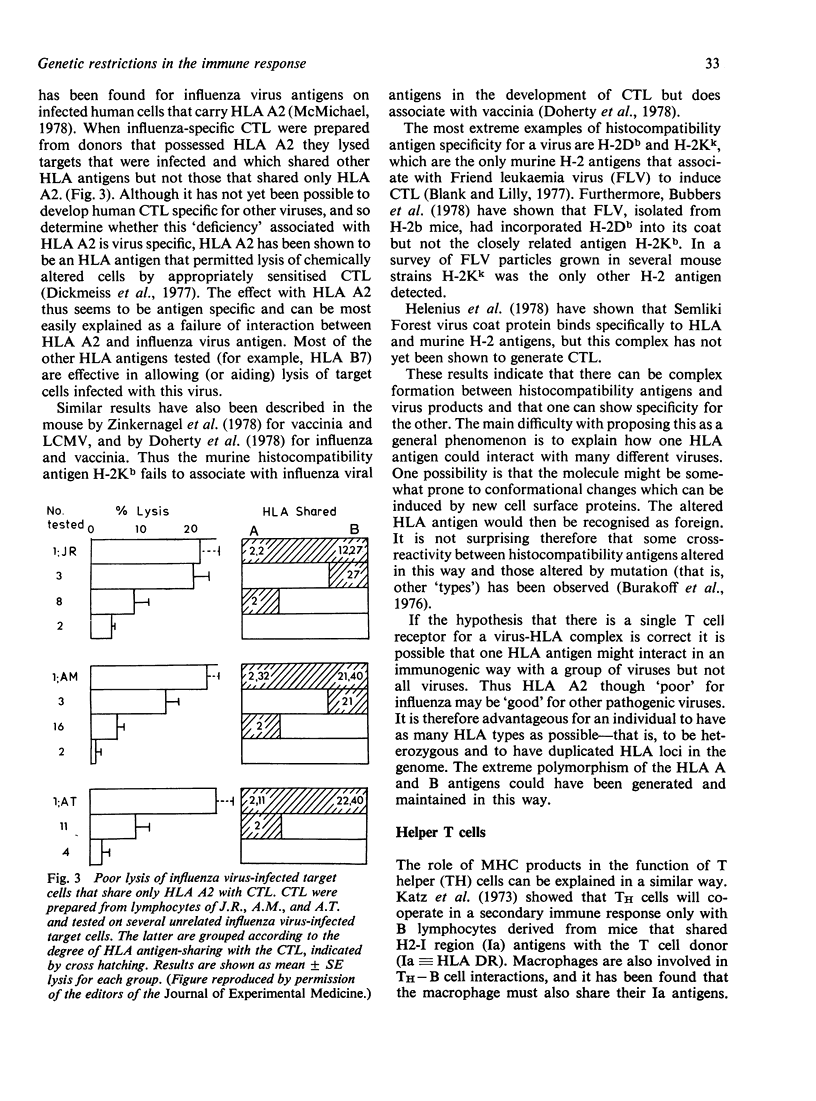
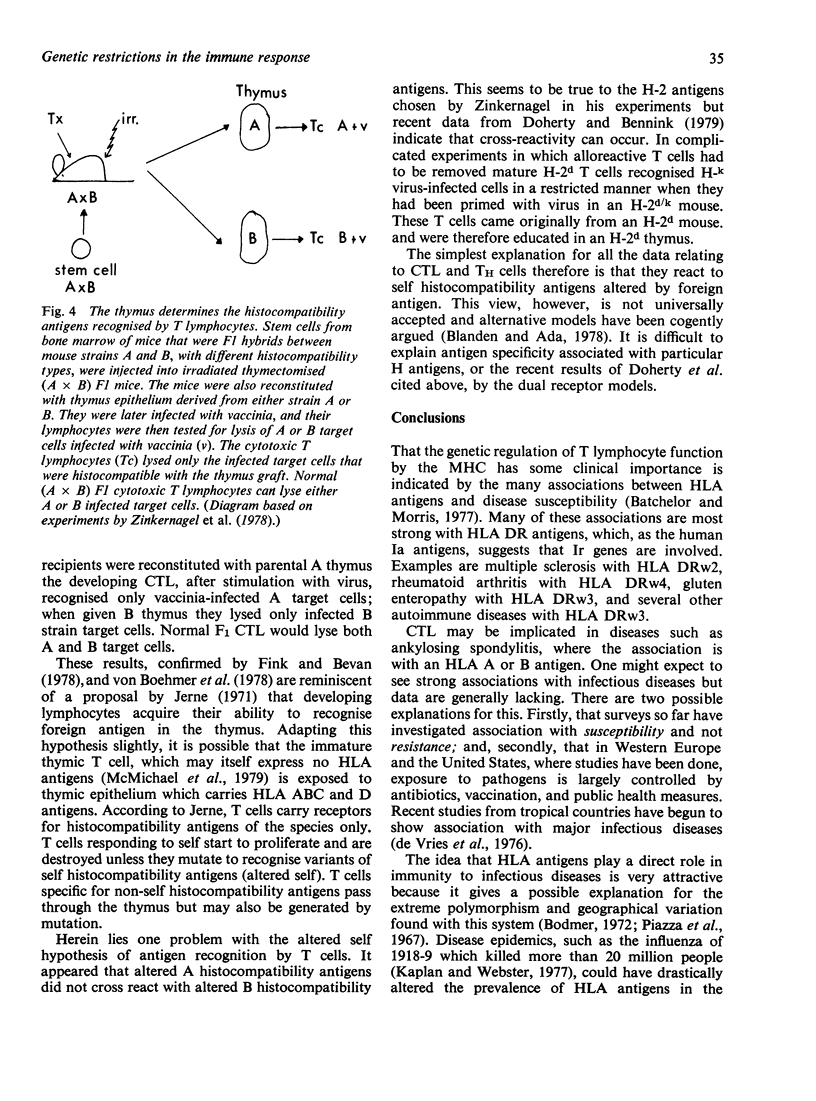
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked immune response genes. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):273–279. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergholtz B. O., Thorsby E. Macrophage-dependent response of immune human T lymphocytes to PPD in vitro. Influence of HLA-D histocompatibility. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(8):779–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Ada G. L. A dual recognition model for cytotoxic T cells based on thymic selection of precursors with low affinity for Self H-2 antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1978 Mar;7(3):181–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank K. J., Lilly F. Evidence for an H-2/viral protein complex on the cell surface as the basis for the H-2 restriction of cytotoxicity. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):808–809. doi: 10.1038/269808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg B., Geckeler W. R., Weigert M. Genetics of the antibody response to dextran in mice. Science. 1972 Jul 14;177(4044):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4044.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. Evolutionary significance of the HL-A system. Nature. 1972 May 19;237(5351):139–passim. doi: 10.1038/237139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubbers J. E., Chen S., Lilly F. Nonrandom inclusion of H-2K and H-2D antigens in Friend virus particles from mice of various strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):340–351. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakoff S. J., Germain R. N., Dorf M. E., Benacerrah B. Inhibition of cell-mediated cytolysis of trinitrophenyl-derivatized target cells by alloantisera directed to the products of the K and D loci of the H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):625–629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickmeiss E., Soeberg B., Svejgaard A. Human cell-mediated cytotoxicity against modified target cells is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):526–528. doi: 10.1038/270526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Bennink J. C. Vaccinia-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses in the context of H-2 antigens not encountered in thymus may reflect aberrant recognition of a virus-H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):150–157. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Biddison W. E., Bennink J. R., Knowles B. B. Cytotoxic T-cell responses in mice infected with influenza and vaccinia viruses vary in magnitude with H-2 genotype. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):534–543. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Blanden R. V., Zinkernagel R. M. Specificity of virus-immune effector T cells for H-2K or H-2D compatible interactions: implications for H-antigen diversity. Transplant Rev. 1976;29:89–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K. Expression and function of idiotypes of lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:195–254. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., McMichael A. J., Batey M. E., McDevitt H. O. A suppressor T cell of the mixed lymphocyte reaction in man specific for the stimulating alloantigen. Evidence that identity at HLA-D between suppressor and responder is required for suppression. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):137–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Bevan M. J. H-2 antigens of the thymus determine lymphocyte specificity. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):766–775. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner I. D., Bowern N. A., Blanden R. V. Cell-medicated cytotoxicity against ectromelia virus-infected target cells. III. Role of the H-2 gene complex. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):122–127. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Sandman R., Diamond L. K. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91950-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Simpson E. Immune-response gene control of cytotoxic T-cell responses to H-Y. Transplant Proc. 1977 Mar;9(1):885–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulmy E., Termijtelen A., Bradley B. A., van Rood J. J. Y-antigen killing by T cells of women is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):544–545. doi: 10.1038/266544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg L. J., Gray E. D., Yunis E. J. Association of HL-A 5 and immune responsiveness in vitro to streptococcal antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):935–943. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansburg D., Briles D. E., Davie J. M. Analysis of the diversity of murine antibodies to dextran B1355. II. Demonstration of multiple idiotypes with variable expression in several strains. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1406–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Morein B., Fries E., Simons K., Robinson P., Schirrmacher V., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Human (HLA-A and HLA-B) and murine (H-2K and H-2D) histocompatibility antigens are cell surface receptors for Semliki Forest virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3846–3850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi T., Mäkelä O. Inheritance of antibody specificity. I. Anti-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl of the mouse primary response. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1498–1510. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. The somatic generation of immune recognition. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Jan;1(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Webster R. G. The epidemiology of influenza. Sci Am. 1977 Dec;237(6):88–106. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1277-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Hamaoka T., Dorf M. E., Maurer P. H., Benacerraf B. Cell interactions between histoincompatible T and B lymphocytes. IV. Involvement of the immune response (Ir) gene in the control of lymphocyte interactions in responses controlled by the gene. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):734–739. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Cramer M., Imanishi-Kari T., Jack R. S., Rajewsky K., Mäkelä O. Isolated hapten-binding receptors of sensitized lymphocytes. I. Receptors from nylon wool-enriched mouse T lymphocytes lack serological markers of immunoglobulin constant domains but express heavy chain variable portions. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):566–573. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Bias W. B., Ishizaka K. Genetic control of basal serum immunoglobulin E level and its effect on specific reaginic sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3588–3592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Askonas B. A. Influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T cells in man; induction and properties of the cytotoxic cell. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Oct;8(10):705–711. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Pilch J. R., Galfré G., Mason D. Y., Fabre J. W., Milstein C. A human thymocyte antigen defined by a hybrid myeloma monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):205–210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Ting A., Zweerink H. J., Askonas B. A. HLA restriction of cell-mediated lysis of influenza virus-infected human cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):524–526. doi: 10.1038/270524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. HLA restriction of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for influenza virus. Poor recognition of virus associated with HLA A2. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1458–1467. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näkelä O., Kaartinen M., Pelkonen J. L., Karjalainen K. Inheritance of antibody specificity V. Anti-2-phenyloxazolone in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1644–1660. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J. H., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. Inter-mouse strain differences in macrophage function and its relationship to antibody responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):159–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Functional specificity of thymus- dependent lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1293–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.320663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Shevach E. M., Thomas D. W., Pickeral S. F., Rosenthal A. S. Genetic restriction in T-lymphocyte activation by antigen-pulse peritoneal exudate cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):571–578. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. S., Rich R. R. Regulatory mechanisms in cell-mediated immune responses. II. A genetically restricted suppressor of mixed lymphocyte reactions released by alloantigen-activated spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1391–1402. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Barcinski M. A., Blake J. T. Determinant selection is a macrophage dependent immune response gene function. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):156–158. doi: 10.1038/267156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Shearer G. M. Bifunctional major histocompatibility-linked genetic regulation of cell-mediated lympholysis to trinitrophenyl-modified autologous lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):914–927. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Paul W. E., Green I. Histocompatibility-linked immune response gene function in guinea pigs. Specific inhibition of antigen-induced lymphocyte proliferation by alloantisera. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1207–1221. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz J. E., Rock K., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. The role of H-2 linked genes in helper T-cell function. II. Isolation on antigen-pulsed macrophages of two separate populations of F1 helper T cells each specific for antigen and one set of parental H-2 products. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):554–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., Takemori T. Properties of primed suppressor T cells and their products. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:106–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theze J., Kapp J. A., Benacerraf B. Immunosuppressive factor(s) extracted from lymphoid cells of nonresponder mice primed with L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 (GAT) III. Immunochemical properties of the GAT-specific suppressive factor. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):839–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Shevach E. M. Nature of the antigenic complex recognized by T lymphocytes: specific sensitization by antigens associated with allogeneic macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2104–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener E., Bandieri A. Differences in antigen handling by peritoneal macrophages from the Biozzi high and low responder lines of mice. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jul;4(7):457–463. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. R. The biological origin of antibody diversity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:467–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Althage A., Cooper S., Kreeb G., Klein P. A., Sefton B., Flaherty L., Stimpfling J., Shreffler D., Klein J. Ir-genes in H-2 regulate generation of anti-viral cytotoxic T cells. Mapping to K or D and dominance of unresponsiveness. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):592–606. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Callahan G. N., Althage A., Cooper S., Klein P. A., Klein J. On the thymus in the differentiation of "H-2 self-recognition" by T cells: evidence for dual recognition? J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):882–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Immunological surveillance against altered self components by sensitised T lymphocytes in lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):547–548. doi: 10.1038/251547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries R. R., Fat R. F., Nijenhuis L. E., van Rood J. J. HLA-linked genetic control of host response to Mycobacterium leprae. Lancet. 1976 Dec 18;2(7999):1328–1330. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91975-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H., Haas W., Jerne N. K. Major histocompatibility complex-linked immune-responsiveness is acquired by lymphocytes of low-responder mice differentiating in thymus of high-responder mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2439–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


