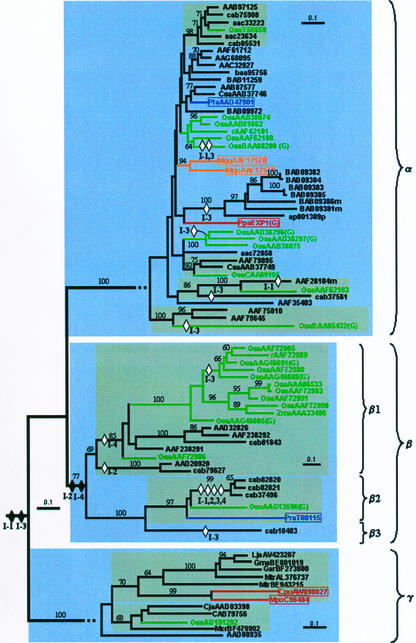
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree for the plant expansin gene family shows an ancient origin of α-, β-, and γ-expansins. Bootstrap values over 60% are indicated above the nodes. The tree was constructed as described in “Materials and Methods.” The major groups are indicated by light-shaded boxes and were strongly supported (>80% bootstrap). Subgroups containing sequences from mixed plant groups in the major branches are further highlighted with dark-shaded boxes. Major plant taxonomic divisions are indicated by accession number color thus: dicot, black; monocot, green; pine, blue; fern, orange; and bryophyte, red. Hypothetical intron gains and losses are indicated as described in Figure 1b. Branches are drawn to scale as indicated by the scale bar (= 0.1 substitutions/1,000 residues). Accession numbers for non-Arabidopsis sequences have a species-specific indentifier as follows: Osa, rice (Oryza sativa); Csa, cucumber (Cucumis sativa); Pta, pine (Pinus taeda); Mqu, Marsilea quadrifolia; Ppa, moss (P. patens); Zma, maize (Zea mays); Pra, Pinus radiata; Lja, Lotus japonicus; Gma, soybean (Glycine max); Gar, Gossypium arborium; Mtr, Medicago truncatula; Cpu, Ceratodon purpureus; Mpo, Marchantia polymorpha; Cja, C. jambhiri; Mcr, common ice plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum).