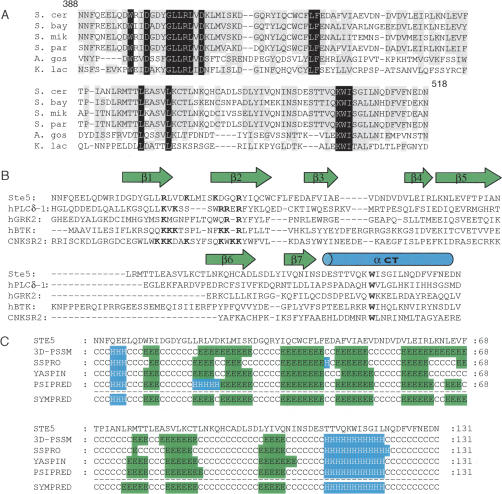
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment and analysis of the predicted S. cerevisiae Ste5 PH domain. (A) Alignment of the S. cerevisiae Ste5 PH domain (residues 388–518) with corresponding sequences in orthologs from Saccharomyces bayanus, Saccharomyces mikatae, Saccharomyces paradoxus, Ashbya gossypii, and Kluyveromyces lactis. (B) Alignment of the S. cerevisiae Ste5 PH domain with selected mammalian PH domains. Secondary structure elements (green arrows, β-strands; blue cylinder, α-helix) depict those in the crystal structure of the PLCδ1 PH domain (Lemmon and Keleti 2005). Basic residues in the β1–β2 loop and the conserved Trp in the C-terminal helix are highlighted (bold). (C) Secondary structure elements in the Ste5 PH domain predicted by the indicated algorithms: 3D-PSSM, SSPro, YAPSIN, PSIPRED, and SYMPRED. (Green/E) β-strand; (blue/H) α-helix; (C) random coil.