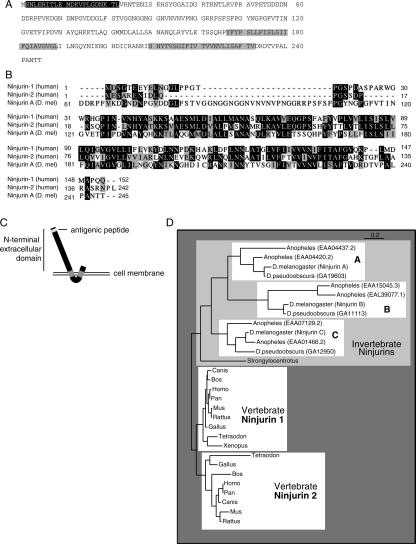
Figure 2.
NijA protein sequence, homology, and topology. (A) Drosophila NijA amino acid sequence, from CG6449. Gray boxes indicate predicted transmembrane domains. The black box indicates the region corresponding to the antigenic peptide. NijA splice form B is shown; isoform A removes VNRT (amino acids 23–26); isoform C removes VPETDDDDNDDRPFV (amino acids 52–66). The cDNA fragment identified by two-hybrid screening encodes amino acids 43–end, consistent with either isoform A or B. (B) ClustalW alignment of human Ninjurin-1 and Ninjurin-2 and Drosophila Ninjurin A. Black boxes indicate identical residues; gray boxes indicate similar residues. Isoform B of NijA is shown, and the human splice forms are the ones reported by Araki and Milbrandt (1996, 2000). (C) Predicted NijA topology, with the termini outside the cell. (D) Phylogenetic tree relating all ninjurin domain-containing proteins identified to date. Non-insect proteins shown are rat Ninjurin-1 and Ninjurin-2, human Ninjurin-1 and Ninjurin-2, BAE34827.1 (Mus musculus), XP 853215.1 (Canis familiaris), XP 528716.1 (Pan troglodytes), XP 586318.2 (Bos taurus), XP 414328.1 (Gallus gallus), NP 001008021.1 (Xenopus tropicalis), CAG06884.1 (Tetraodon nigroviridis), XP 416382.1 (Gallus gallus), XP 854702.1 (Canis familiaris), CAF97213.1 (Tetraodon nigroviridis), XP 522310.1 (Pan troglodytes), XP 586544.2 (Bos taurus), and XP 783902.1 (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus).